GRASS 6 Tutorial/Vector spatial analysis: Difference between revisions
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
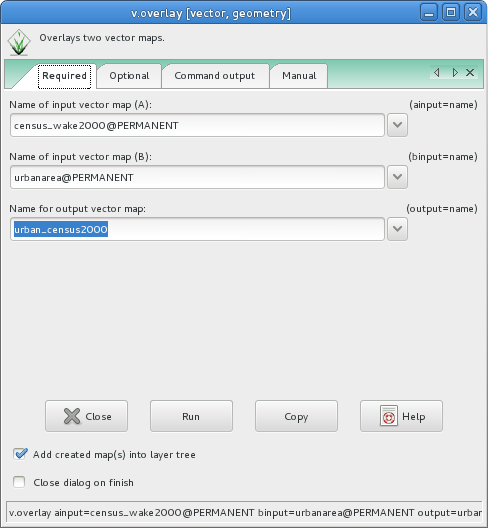
The above examples can be easily replicated using the <code>v.overlay</code> GUI, avaialble under 'Vector --> Overlay Vector Maps --> Overlay Vector Maps [v.overlay]' | The above examples can be easily replicated using the <code>v.overlay</code> GUI, avaialble under 'Vector --> Overlay Vector Maps --> Overlay Vector Maps [v.overlay]' | ||
[[File: Voverlay_gui.png|300px|center]] | |||
Revision as of 09:54, 29 July 2013
Vector Spatial Analysis
The following examples demonstrate how basic vector data processing operations, such as overlay, union and clipping can be performed in GRASS 6.4. These operations are all performed using the GRASS module, v.overlay, which can either be run using the GUI or from the command-line interface. The following examples are demonstrated using the CLI, using two vector datasets, namely: urbanarea and census_wake2000 from the North Carolina database.
d.mon start=x0 g.region vect=census_wake2000 d.vect census_wake2000 col=blue d.vect urbanarea col=red type=boundary
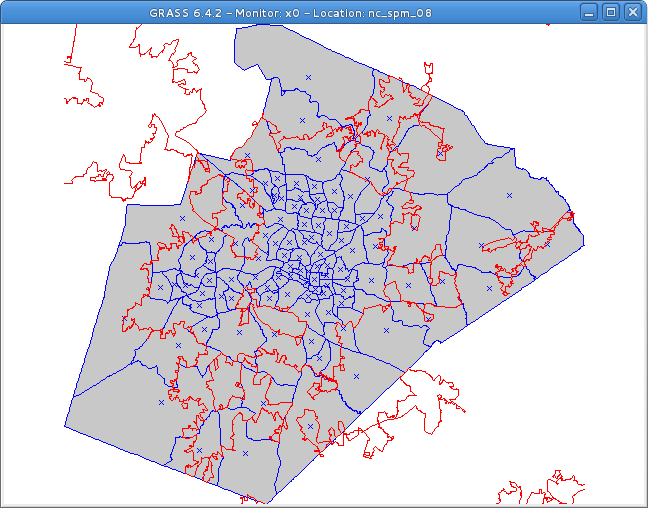
Vector Union
The following command creates a union (operator or) of the two polygon vectors:
v.overlay ain=census_wake2000 bin=urbanarea out=urban_census2000 operator=or
with urban_census2000 created as follows.
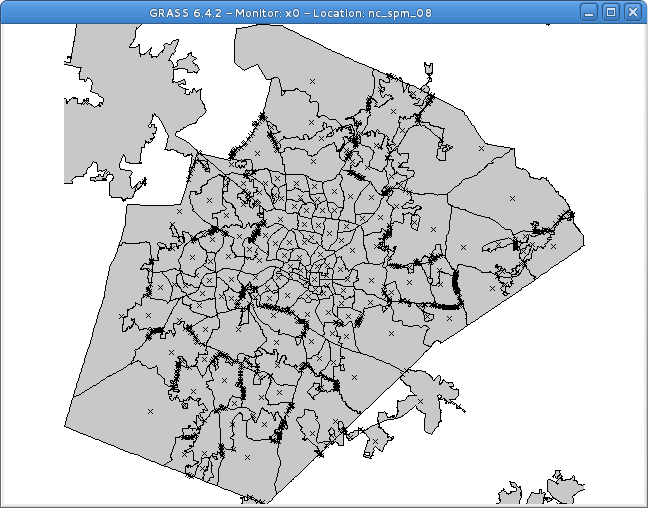
Vector Intersection
The following command creates an intersection (operator and) of the two polygon vectors:
v.overlay ain=census_wake2000 bin=urbanarea out=urban_census2000_intersect operator=and
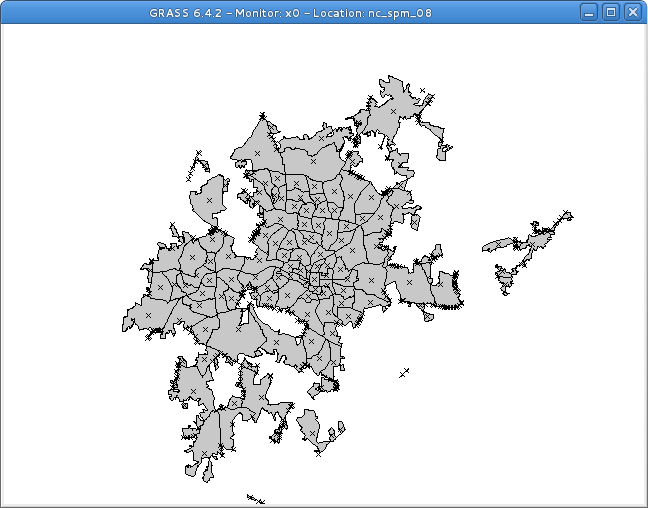
Vector Clip
The following command clips (cuts out) intersection (operator not) of the two polygon vectors:
v.overlay ain=census_wake2000 bin=urbanarea out=urban_census2000_intersect operator=not
Vector Analysis using the GUI
The above examples can be easily replicated using the v.overlay GUI, avaialble under 'Vector --> Overlay Vector Maps --> Overlay Vector Maps [v.overlay]'