Software requirements specification: Difference between revisions
(updated) |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
=== Functional requirements === | === Functional requirements === | ||
GRASS GIS 7 does not have any special functional requirements. | |||
=== Performance requirements === | === Performance requirements === | ||
GRASS GIS runs from low-end to high-end hardware. | GRASS GIS runs from low-end to high-end hardware (32bit/64bit). | ||
Concerning the software capabilities and limits, see [[GRASS GIS Performance]]. | Concerning the software capabilities and limits, see [[GRASS GIS Performance]]. | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
=== Logical database requirement === | === Logical database requirement === | ||
GRASS GIS uses its internal (but public, see [http://grass.osgeo.org/programming7 here]) database structure. | |||
=== Software System attributes === | === Software System attributes === | ||
No special requirements. | |||
=== Other requirements === | === Other requirements === | ||
No special requirements. | No special requirements. | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 18 January 2013
This list is following the Wikipedia article Software_requirements_specification.
Introduction
Commonly referred to as GRASS, this is free Geographic Information System (GIS) software used for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, graphics/maps production, spatial modeling, and visualization. GRASS GIS is currently used in academic and commercial settings around the world, as well as by many governmental agencies and environmental consulting companies. GRASS GIS is an official project of the Open Source Geospatial Foundation.
Purpose
GRASS GIS, a multi-purpose Open Source GIS, can be used for geospatial data production, analysis, and mapping. It handles 2D and 3D (voxel) raster data, provides a topological 2D and 3D vector engine with SQL-based attribute management, and vector network analysis functions. The database backend may be chosen from a file-based DBF tables, SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and ODBC data sources. GRASS GIS offers many spatial modelling algorithms, 3D visualization, as well as image processing routines pertaining to LiDAR and multi-band imagery. GRASS integrates well with other Open Source and proprietary software packages for geostatistical analysis, cartographic output, and Web GIS applications.
Definitions
- GIS: Geographic Information System
- GPL: GNU General Public License
System overview
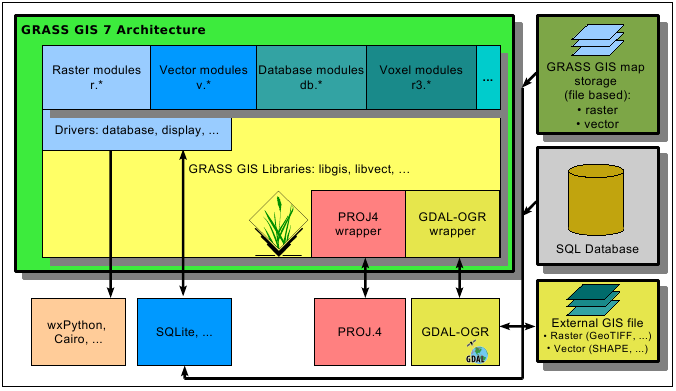
GRASS GIS is written in a fully modular way which minimizes overhead (see Figure below). This allows users to run the system, or parts of it, even in portable smart devices, or effectively scale it up to process massive datasets which exceed available system memory by orders of magnitudes. The latest stable release provides 425 modules (commands) for data management and analysis. GRASS GIS can be installed centrally on a network directory for multi-user usage.
Project Metrics provided by Ohloh.
{{#widget:Ohloh Project|id=3666|type=partner_badge}}
The modules are organized firstly by category (general GIS management modules: g.*, vector modules: v.*, raster modules: r.*, 3D raster modules: r3.*, image processing: i.*, database management: db.*, cartography modules ps.*, etc.) and secondarily by function ("in" input modules, "out" output modules, "cost" cost surfaces, "network" network analysis, etc.). This categorization helps the user to navigate easily in the wealth of available tools, also supported by a tree based functionality catalogue in the graphical user interface.
Data management: The GRASS GIS data directory can be either stored in the user's home directory, or, for shared access for teams the data directory can also be stored in a shared network directory. Users have exclusive write access to their own data while read access to the other team members is granted (can be individually revoked as needed).
References
- GRASS Development Team, 2012. Geographic Resources Analysis Support System (GRASS 7) Programmer's Manual. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Electronic document: http://grass.osgeo.org/programming7/
- Neteler, M., Bowman, M.H., Landa, M., Metz, M., 2012, GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose open source GIS. Environmental Modelling & Software (DOI | PDF)
- Neteler, M. and H. Mitasova, 2008, Open Source GIS: A GRASS GIS Approach. 3rd Ed. 406 pp, 80 illus., Springer, New York. Online Supplement: http://www.grassbook.org/
Overall description
GRASS GIS (Geographic Resources Analysis Support System) is a free, open source geographical information system (GIS) capable of handling raster, topological vector, image processing, and graphic data.
Product perspective
TBD.
Product functions
- Intro projections and spatial transformations
- Intro 2D raster map processing
- Intro 3D raster map (voxel) processing
- Intro image processing
- Intro vector map processing and network analysis
- Intro database management
- Intro Temporal processing
- Printing
- Index of topics
Overall: GRASS GIS Manual
User characteristics
GRASS GIS is a multi-purpose Open Source GIS. It addresses beginners as well as experts, from academia to practitioners in government and industry.
Constraints, assumptions and dependencies
GRASS GIS runs on MS-Windows, Mac OSX, GNU/Linux and other POSIX compliant platforms.
Specific requirements
External interface requirements
Requirements to compile GRASS GIS 7: see here
Functional requirements
GRASS GIS 7 does not have any special functional requirements.
Performance requirements
GRASS GIS runs from low-end to high-end hardware (32bit/64bit).
Concerning the software capabilities and limits, see GRASS GIS Performance.
Design constraints
GRASS GIS can be run in both command line/scripted/embedded as well as interactive mode (graphical user interface).
Logical database requirement
GRASS GIS uses its internal (but public, see here) database structure.
Software System attributes
No special requirements.
Other requirements
No special requirements.
