Vector Database Management: Difference between revisions
m (added link to progman) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''This page is a work in progress.<BR>Please contribute if you have experience with anything that is still poorly documented.'' | ''This page is a work in progress.<BR>Please contribute if you have experience with anything that is still poorly documented.'' | ||
==Vector data processing== | ''Looking for vector geometry management? See [[:Category:Vector|here]]'' | ||
== GRASS GIS vector management model == | |||
The GRASS GIS vector management model allows to link map objects to database management systems (DBMS). In this short section, we try to give an overview on how GRASS matches map features and attributes. | |||
Consider creating a map where you would handle (i) parcels with various crops, (ii) a set of owners for these parcels, and (iii) paths to access them. The latter are determined by limits between contiguous fields. | |||
One could decide to store data in several distinct maps, e.g.: | |||
* a map "path" containing lines, to describe paths; | |||
* a map "crop" containing areas, to describe crops; | |||
* a map "owner" containing areas, to describe owners. | |||
We can point several drawbacks to this method: | |||
* we induce redundancy of geometric features between maps "crop" and "owner". Even though their attributes are independent, areas share the same geometry; | |||
* topological relation between paths and parcels limits won't be ensured when it's about to modify the shape of parcels. | |||
=== The concept of layers === | |||
A better solution will resort to the concept of ''layers''. A single vector map will store geometric features, while several tables in the DBMS will handle attribute contents. Figure 1 shows how it works. Let's comment this sketch. | |||
[[File:Catsnlayers.png|800px|thumb|alt=cats and layers in GRASS GIS|center|Figure 1]] | |||
This vector map contains ''boundaries'' and ''centroids'', that determine ''areas'' (see {{cmd|vectorintro}}). Boundaries are used as linear features to hold tracks geometry. Each feature is automatically assigned an ''internal identifier'' as soon as it is added to the map. The user cannot edit this ''id'', GRASS GIS handles it for you, and ensures the uniqueness of each ''id''. Here, ''id''s 1 to 12 are assigned to boundaries, ''id''s 13 to 17 correspond to centroids. | |||
We could consider using this ''key-id'' to directly point at remote attribute records in a table. But GRASS provides a more flexible method, based on the ability : | |||
* to give either a single ''identifier'' to each feature or to group similar features by giving them all a common ''identifier''; | |||
* to give several ''identifiers'' to an object if it is related to multiple thematic data. | |||
These ''identifiers'' are named '''categories''', they are organised in as many sets as you wish, that are named '''layers'''. | |||
=== The concept of categories === | |||
In this example (and above sketch) objects are categorized according to three layers. Boundaries have categories in layer 1, centroids have categories in layers 2 and 3. Note : | |||
* 3 boundaries share category 5 within layer 1; | |||
* among others, object with id 7 has zero category. | |||
Command {{cmd|v.category}} allows to maintain vector categories. | |||
Layer 1 connects the map with a table named "paths", "cat" is the key column for this relation. The name of the key column may be different, e.g. "code" for layer 2 and table "plots". Note : | |||
* layer 3 does not refer to any table in the database; | |||
* "code" value 34 within table "plots" has no corresponding category in layer 2; | |||
* category 14 in layer 1 does not refer to any "cat" value in table "paths"; | |||
* database contains a table named "owner" which is not related to any layer. | |||
Database management in GRASS GIS is provided by the db.* set of commands : | |||
* database connections ({{cmd|db.connect}}, {{cmd|db.login}}); | |||
* SQL operations ({{cmd|db.select}}, {{cmd|db.execute}}, etc.), while v.db.* set of commands allows to manage linked tables to a vector map: | |||
* layers can be listed/maintained ({{cmd|v.db.connect}}); | |||
* some v.db.* commands are simply {{cmd|db.execute}} frontends ({{cmd|v.db.addcol}}, {{cmd|v.db.join}}, etc.). | |||
{{cmd|v.to.db}} is the command that allows to populate a table attached to a given vector layer; not only categories can be uploaded, but geometric data too (area, perimeter, ccordinates, etc.). | |||
==Vector attribute data processing== | |||
* See the GRASS {{cmd|vectorintro}} vector data processing help page. | * See the GRASS {{cmd|vectorintro}} vector data processing help page. | ||
* See also the GRASS {{cmd|databaseintro}} Database management help page. | * See also the GRASS {{cmd|databaseintro}} Database management help page. | ||
* See also the [[Openoffice.org with SQL Databases]] wiki page | * See also the [[Openoffice.org with SQL Databases]] wiki page | ||
===Database Support=== | ===Database Support=== | ||
Since GRASS GIS 7.x, SQLite is the default (local) DB driver used for GRASS vector attribute management. | |||
==== SQLite ==== | |||
SQLite is a local database format, but much more featureful than DBF (see below). It basically combines the power of real SQL databases with the advantage of local data storage (no server needed). A nice tool to directly work in the SQLite database is [https://sqlitebrowser.org/ SQLite Database Browser]. | |||
Since GRASS 7, SQLite is the default (local) DB used for the vector attribute management. | |||
* GRASS {{cmd|grass- | * GRASS {{cmd|grass-sqlite}} SQLite driver help page | ||
* [http://www.sqlite.org SQLite Homepage] | |||
==== | ==== ASCII text (.csv, etc.) ==== | ||
ASCII vector data exchange: | |||
* {{cmd|v.in.ascii}} module help page | |||
* {{cmd|v.out.ascii}} module help page | |||
If your .csv file contains "quoted" strings containing commas, you can use the [[AddOns#Miscellaneous_Add-ons|csv_dequote.pl]] script to parse them into a less-problematic form ready for import with {{cmd|v.in.ascii}}. | |||
==== MySQL ==== | ==== MySQL ==== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 85: | ||
* GRASS {{cmd|grass-pg}} PostgreSQL driver page | * GRASS {{cmd|grass-pg}} PostgreSQL driver page | ||
* [http://www.postgresql.org PostgreSQL Homepage] | * [http://www.postgresql.org PostgreSQL Homepage] | ||
==== DBF ==== | |||
In GRASS 6, DBF was the default (local) DB used for GRASS vector attributes. It is easy to use but with the simplicity comes limited features. Such limits are 10 chars per column name and no support for SQL calculations in SELECT statements. | |||
* GRASS {{cmd|grass-dbf}} DBF driver help page | |||
==== FileMaker Pro ==== | ==== FileMaker Pro ==== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 163: | ||
** The {{cmd|v.to.db}} module | ** The {{cmd|v.to.db}} module | ||
== More Help == | |||
* {{cmd|database}} module help pages | * {{cmd|database}} module help pages | ||
* {{cmd|vector}} module help pages | * {{cmd|vector}} module help pages | ||
* GRASS {{cmd|sql}} query help page | * GRASS {{cmd|sql}} query help page | ||
* [https://grass.osgeo.org/programming8/vectorlib.html Vectorlib in the GRASS GIS 8 Programmer's Manual] | |||
* [http://grass.osgeo.org/grass57/tutorial/links.html SQL reference links] | * [http://grass.osgeo.org/grass57/tutorial/links.html SQL reference links] | ||
* [http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysqld-version-reference/en/mysqld-version-reference-reservedwords-5-0.html MySQL reserved words list] | * [http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysqld-version-reference/en/mysqld-version-reference-reservedwords-5-0.html MySQL reserved words list] | ||
* https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/61927/what-is-the-difference-between-node-and-vertex-in-gis | |||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
[[Category:Vector]] | [[Category:Vector]] | ||
[[Category:database]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:37, 10 October 2023
This page is a work in progress.
Please contribute if you have experience with anything that is still poorly documented.
Looking for vector geometry management? See here
GRASS GIS vector management model
The GRASS GIS vector management model allows to link map objects to database management systems (DBMS). In this short section, we try to give an overview on how GRASS matches map features and attributes.
Consider creating a map where you would handle (i) parcels with various crops, (ii) a set of owners for these parcels, and (iii) paths to access them. The latter are determined by limits between contiguous fields.
One could decide to store data in several distinct maps, e.g.:
- a map "path" containing lines, to describe paths;
- a map "crop" containing areas, to describe crops;
- a map "owner" containing areas, to describe owners.
We can point several drawbacks to this method:
- we induce redundancy of geometric features between maps "crop" and "owner". Even though their attributes are independent, areas share the same geometry;
- topological relation between paths and parcels limits won't be ensured when it's about to modify the shape of parcels.
The concept of layers
A better solution will resort to the concept of layers. A single vector map will store geometric features, while several tables in the DBMS will handle attribute contents. Figure 1 shows how it works. Let's comment this sketch.
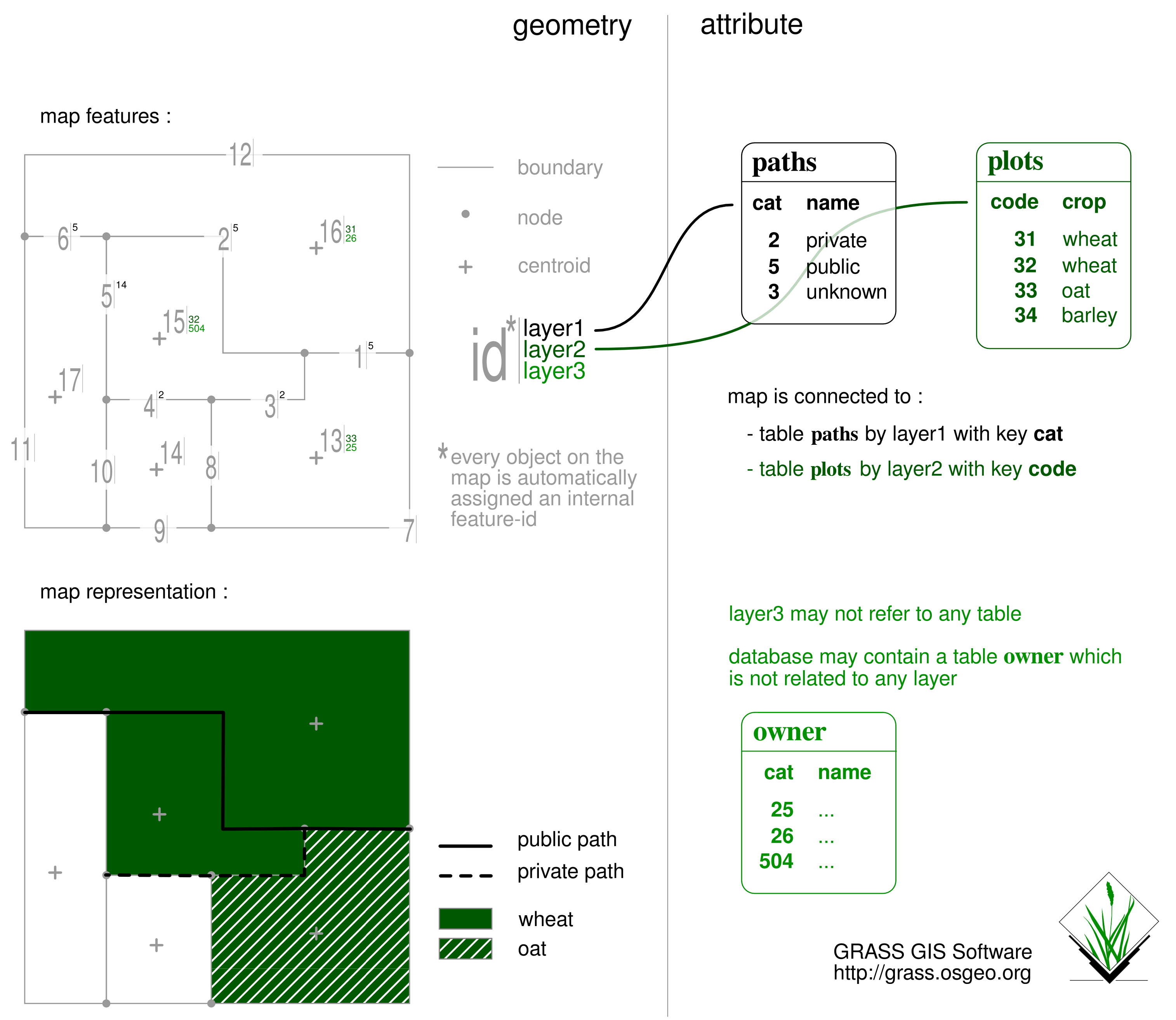
This vector map contains boundaries and centroids, that determine areas (see vectorintro). Boundaries are used as linear features to hold tracks geometry. Each feature is automatically assigned an internal identifier as soon as it is added to the map. The user cannot edit this id, GRASS GIS handles it for you, and ensures the uniqueness of each id. Here, ids 1 to 12 are assigned to boundaries, ids 13 to 17 correspond to centroids.
We could consider using this key-id to directly point at remote attribute records in a table. But GRASS provides a more flexible method, based on the ability :
- to give either a single identifier to each feature or to group similar features by giving them all a common identifier;
- to give several identifiers to an object if it is related to multiple thematic data.
These identifiers are named categories, they are organised in as many sets as you wish, that are named layers.
The concept of categories
In this example (and above sketch) objects are categorized according to three layers. Boundaries have categories in layer 1, centroids have categories in layers 2 and 3. Note :
- 3 boundaries share category 5 within layer 1;
- among others, object with id 7 has zero category.
Command v.category allows to maintain vector categories.
Layer 1 connects the map with a table named "paths", "cat" is the key column for this relation. The name of the key column may be different, e.g. "code" for layer 2 and table "plots". Note :
- layer 3 does not refer to any table in the database;
- "code" value 34 within table "plots" has no corresponding category in layer 2;
- category 14 in layer 1 does not refer to any "cat" value in table "paths";
- database contains a table named "owner" which is not related to any layer.
Database management in GRASS GIS is provided by the db.* set of commands :
- database connections (db.connect, db.login);
- SQL operations (db.select, db.execute, etc.), while v.db.* set of commands allows to manage linked tables to a vector map:
- layers can be listed/maintained (v.db.connect);
- some v.db.* commands are simply db.execute frontends (v.db.addcol, v.db.join, etc.).
v.to.db is the command that allows to populate a table attached to a given vector layer; not only categories can be uploaded, but geometric data too (area, perimeter, ccordinates, etc.).
Vector attribute data processing
- See the GRASS vectorintro vector data processing help page.
- See also the GRASS databaseintro Database management help page.
- See also the Openoffice.org with SQL Databases wiki page
Database Support
Since GRASS GIS 7.x, SQLite is the default (local) DB driver used for GRASS vector attribute management.
SQLite
SQLite is a local database format, but much more featureful than DBF (see below). It basically combines the power of real SQL databases with the advantage of local data storage (no server needed). A nice tool to directly work in the SQLite database is SQLite Database Browser. Since GRASS 7, SQLite is the default (local) DB used for the vector attribute management.
- GRASS grass-sqlite SQLite driver help page
- SQLite Homepage
ASCII text (.csv, etc.)
ASCII vector data exchange:
- v.in.ascii module help page
- v.out.ascii module help page
If your .csv file contains "quoted" strings containing commas, you can use the csv_dequote.pl script to parse them into a less-problematic form ready for import with v.in.ascii.
MySQL
- GRASS grass-mysql MySQL driver page
- GRASS grass-mesql MSQL embedded driver page
- MySQL Homepage
PostgreSQL
- GRASS grass-pg PostgreSQL driver page
- PostgreSQL Homepage
DBF
In GRASS 6, DBF was the default (local) DB used for GRASS vector attributes. It is easy to use but with the simplicity comes limited features. Such limits are 10 chars per column name and no support for SQL calculations in SELECT statements.
- GRASS grass-dbf DBF driver help page
FileMaker Pro
William Kyngesburye wrote on the grass-user mailing list:
I think the key to access FileMaker DBs from GRASS is that the FileMaker ODBC connector is for OSX's iODBC, not UnixODBC.
GRASS 6 has an iODBC configure option. It's the same --with- odbc-* options, it just tries iodbc if it can't find unixodbc.
Oracle
This has been reported to work. Try ODBC and search the mailing list archive. The connection is done via OGR.
ODBC
- External DB support via ODBC (e.g. FileMaker Pro)
- unixODBC is required to make it work
- to configure you could use the graphical frontend ODBCConfig to configure your ODBC connection.
Example-entry in ~/.odbc.ini for usage of ODBC with PostgreSQL
[dbname] Description = PostgreSQL database for my project Driver = postgres Trace = No TraceFile = Database = mydb Servername = myserver UserName = myusername Password = mysecretpasswd Port = 5432 Protocol = 9.0.3 ReadOnly = No RowVersioning = No ShowSystemTables = No ShowOidColumn = No FakeOidIndex = No ConnSettings =
Additionall you need to define the libraries to use for the different drivers in /etc/odbcinst.ini.
[postgres] Description = ODBC for postgres Driver = /usr/lib/unixODBC/libodbcpsql.so Setup = /usr/lib/unixODBC/libodbcpsqlS.so FileUsage = 1
- GRASS grass-odbc ODBC driver page
Concepts and jargon
- GRASS 6 Terminology
- Table
- Table column
- Table row
- Vector map layer
- Each vector file has a special data field named "cat" (derived originally from "category"), filled with integers, that serves to identify each vector object. The 'cat' field also serves as a "key field" that can link each vector object with a corresponding record in an attributes table of a database (NB: 'cat' values do NOT have to be unique for vector objects, but DO have to be unique in an attributes table, permitting both one-to-one and many-to-one relationships). The attributes table must contain a key field, filled with integers (only integers are permitted to serve as key fields in GRASS), that matches the values in the vector 'cat' field.
- A vector can be linked with more than one attribute table, using LAYERS. By default, every vector file has a LAYER 1 with a 'cat' field, filled with integers to identify each vector object. Additional *LAYERS*, along with their associated 'cat' fields, can be created using v.category. Each LAYER has its own independent 'cat' field that can be used to link with a separate attributes table.
- For example, a vector file of cities can have *LAYER 1* whose 'cat' field links the vector points with an attributes table of demographic data; it can also have a LAYER 2, with an associated 'cat' field (independent of the 'cat' field of LAYER 1), linked to a different attributes table of economic data. Values in the 'cat' fields of different LAYERS can be the same or different. The 'cat' values and linked attributes table can be queried independently for each LAYER. In the example, one can query the cities by population from the demographics attributes table linked with the 'cat' field of LAYER 1, or query the cities by household income from the economic attributes table linked with the same vector points through the 'cat' field of LAYER 2. _MichaelBarton - 12 Nov 2005_
Common tasks
Background info find in vectorintro Vector data processing in GRASS GIS.
- Connect a DB (db.connect, v.db.connect)
- Copy a table (db.copy)
- Copy selected columns from a table
- Create a new table (v.db.addtable)
- Create a new column (v.db.addcol)
- Extract data via SQL query (v.extract, db.select)
- Low level access to DB
- The db.execute module
- Populate a DB (v.db.update etc.)
- The v.to.db module
More Help
- database module help pages
- vector module help pages
- GRASS sql query help page
- Vectorlib in the GRASS GIS 8 Programmer's Manual
- SQL reference links
- MySQL reserved words list
- https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/61927/what-is-the-difference-between-node-and-vertex-in-gis