GRASS 6 Tutorial/Raster data management: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Raster data management== ===Overview=== This section of the tutorial is intended to provide new users with an introduction to raster data management in GRASS GIS. As with o...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Raster data management== | ==Raster data management== | ||
=== | ===Data Import=== | ||
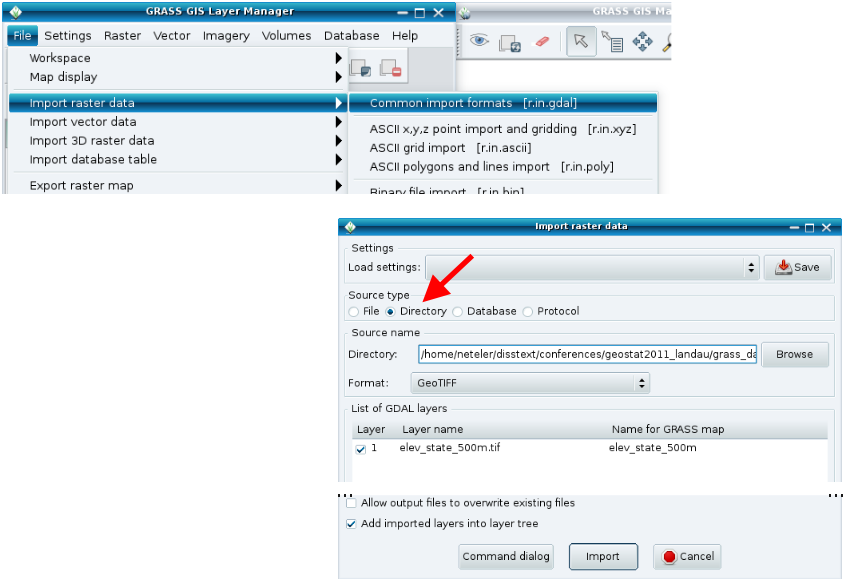
In a similar way to the vector data management, the import and export of raster data is underpinned by GDAL. As such, the modules, <code>r.in.*</code> and <code>r.out.*</code> and specifically, <code>r.in.gdal</code> and <code>r.out.gdal</code> are used. The module <code>r.extenal</code> can be used in lieu of importing a raster into GRASS. | |||
A Geotiff can be imported into GRASS using the command line (input represents the full or relative path to the raster file you want to import; output is its raster name in GRASS). The same can be achieved using the GUI. | |||
r.in.gdal input=elev_input_state500m.tif output=elev_input_state500m | |||
[[File:Grass raster import.png|400px]] | |||
Sometimes, you need to define the region of the Mapset to the extent of your raster. For instance, using the above-mentioned example, you would simply: | |||
g.region rast=elev_input_state500m | |||
A common issue that users are faced with is how to import several GeoTiffs? Obviously the above steps can be repeated using the GUI or copy-pasting the command line or more simply using the following BASH for loop: | |||
for file in `ls *.tif` | |||
do | |||
r.in.gdal input=$file output=${file%.tif} | |||
done | |||
''Note - that when you run r.in.gdal, the full extent of the map is imported'' | |||
[[Category: Tutorial]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:47, 9 August 2013
Raster data management
Data Import
In a similar way to the vector data management, the import and export of raster data is underpinned by GDAL. As such, the modules, r.in.* and r.out.* and specifically, r.in.gdal and r.out.gdal are used. The module r.extenal can be used in lieu of importing a raster into GRASS.
A Geotiff can be imported into GRASS using the command line (input represents the full or relative path to the raster file you want to import; output is its raster name in GRASS). The same can be achieved using the GUI.
r.in.gdal input=elev_input_state500m.tif output=elev_input_state500m
Sometimes, you need to define the region of the Mapset to the extent of your raster. For instance, using the above-mentioned example, you would simply:
g.region rast=elev_input_state500m
A common issue that users are faced with is how to import several GeoTiffs? Obviously the above steps can be repeated using the GUI or copy-pasting the command line or more simply using the following BASH for loop:
for file in `ls *.tif`
do
r.in.gdal input=$file output=${file%.tif}
done
Note - that when you run r.in.gdal, the full extent of the map is imported