Installation Guide: Difference between revisions
⚠️HuidaeCho (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (70 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== General == | == General == | ||
:''Note: For compilation of GRASS GIS source code, see [[Compile and Install]]'' | |||
This page explains the installation of GRASS binaries. | |||
GRASS GIS requires a workstation running either some flavor of UNIX conforming to POSIX standards like Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, IRIX, or BSD or MS-Windows. It is also possible to run GRASS in MS Windows by using UNIX translation software such as [[Cygwin]] or natively with MingGW. Ideally, you should have at least 500 Mb for data and 512 Mb RAM. The source code package needs around 270 MB uncompressed. The resulting binaries may need between 20 MB and 180 MB depending on your platform. During a full compilation you may need temporarily up to 150MB including the source code. | |||
The [https://grass.osgeo.org/download/ Software Download Section] of the main GRASS web site contains the latest binaries and source code for all supported platforms. That site also has general directions for installing GRASS manually. However, installation is slightly different on each operating system. Here you can find user-contributed pointers for installing GRASS on specific platforms. In particular, many operating systems have package management utilities that can greatly simplify GRASS installation. | |||
== MS Windows == | |||
The [ | :''The official download page [https://grass.osgeo.org/download/windows/ GRASS GIS for MS-Windows]'' | ||
There are two main flavours: | |||
* '''OSGeo4W installer''', for a broad set of open source geospatial software packages including GRASS GIS as well as many other packages (QGIS, GDAL/OGR, and more). Advantage: whenever you run again the OSGeo4W installer, it updates the existing installation. | |||
* '''Standalone winGRASS installer''': install GRASS GIS with the required support packages. | |||
=== OSGeo4W installer === | |||
OSGeo4W is an installer for a broad set of open source geospatial software packages including GRASS GIS as well as many other packages (QGIS, GDAL/OGR, and more). Advantage: whenever you run again the OSGeo4W installer, it updates the existing installation. | |||
* Install using [https://trac.osgeo.org/osgeo4w/ OSGeo4W installer] which installs all dependencies as well (PROJ, GDAL, GEOS, Python, etc.) | |||
==== Launch the OSGeo4W installer ==== | |||
Save the downloaded installer (consider to keep it for future updates) and run it as an ''administrator''. | |||
You can select either the grass (stable) or grass-daily (development) packages to install., | |||
[[Image:Osgeo4w_1.png|center|thumb|500px|Install with "Administrator" rights]] | |||
==== Variant A) Express installation ==== | |||
Use "Express Desktop Install" mode to select stable version. | |||
[[Image:Osgeo4w_2_express.png|center|thumb|500px|Use "Express installation" to select stable version]] | |||
[[Image:Osgeo4w_3_express.png|center|thumb|500px]] | |||
Common installed Python packages: | |||
* python3-gdal | |||
* python3-matplotlib | |||
* python3-wx | |||
* python3-numpy | |||
* python3-pillow | |||
* python3-pip | |||
* python3-ply | |||
* python3-pyopengl | |||
* python3-psycopg2 | |||
* python3-six | |||
* python3-pywin32 | |||
Additional useful packages (e.g. python3-pandas, msys) can be installed in "Advanced Install" mode. | |||
==== Variant B) Advanced installation ==== | |||
Use "Advanced Install Mode" to select development version. | |||
[[Image:Osgeo4w_2_advanced.png|center|thumb|500px|Use "Advanced installation" to select development version]] | |||
[[Image:Osgeo4w_3_advanced.png|center|thumb|500px]] | |||
=== winGRASS standalone installer === | |||
* Native winGRASS package installer is available [https://grass.osgeo.org/grass-stable/binary/mswindows/native/ here]. | |||
=== QGIS with winGRASS installer === | |||
* QGIS including native winGRASS packages are provided [https://www.qgis.org/wiki/Download here]. | |||
== GNU/Linux == | == GNU/Linux == | ||
:''The official page [https://grass.osgeo.org/download/linux/ GRASS GIS Download for GNU/Linux]'' | |||
=== Debian === | === Debian === | ||
| Line 16: | Line 77: | ||
apt-get install grass grass-doc | apt-get install grass grass-doc | ||
This is the easiest way to install GRASS on Debian. If you choose to install a binary version manually from the main web site, be sure to follow the instructions for making symlinks found as a note to the [[ | This is the easiest way to install GRASS on Debian. If you choose to install a binary version manually from the main web site, be sure to follow the instructions for making symlinks found as a note to the [[https://grass.osgeo.org/grass-stable/binary/linux/snapshot/ GRASS GIS stable weekly snapshot]] release. | ||
==== DebianGIS ==== | |||
There is also the wonderful [https://wiki.debian.org/DebianGis DebianGIS] project which has a more recent GRASS version with its related packages. Read here for more [[GRASS in Debian |details]] | |||
==== | ==== Compiling GRASS from source ==== | ||
* See [[Compile and Install]] of Source Code | |||
=== Installation on Fedora === | |||
The [https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/grass Fedora project] provides RPM-packages for stable releases prepared to install on Fedora systems: | |||
= | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo dnf install grass grass-gui | |||
</source> | |||
=== Mageia === | |||
* [https://madb.mageia.org/package/show/name/grass/ Mageia] provides PROJ/GDAL/GRASS RPMs: | |||
urpmi grass | |||
=== | === openSUSE === | ||
[ | * [https://build.opensuse.org/package/show/Application:Geo/grass openSUSE] provides GRASS and related RPM-packages: | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo zypper refresh | |||
sudo zypper install grass | |||
</source> | |||
Alternatively, one can use the '''One-Click installer''': | |||
https://software.opensuse.org/package/grass | |||
=== Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL, CentOS and EPEL) === | |||
* [https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/grass Fedora] offers GRASS and related binaries for CentOS and EPEL | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
dnf install grass | |||
</source> | |||
=== Ubuntu === | === Ubuntu === | ||
| Line 60: | Line 131: | ||
To get the latest version of GRASS on Ubuntu, compile the code from source. See the [[Compile and Install]] section for a shell script that makes this easy. | To get the latest version of GRASS on Ubuntu, compile the code from source. See the [[Compile and Install]] section for a shell script that makes this easy. | ||
== | == MacOS == | ||
Precompiled GRASS GIS packages for macOS can be found [https://grass.osgeo.org/download/mac here]. These are distributed as zipped *.dmg packages. Opening the dmg prompts the user to simply drag and drop the app into the Applications folder. In fact, they '''must''' be installed into the Applications folder and may not run properly in other locations. | |||
A brief introduction to how to install via [https://www.macports.org MacPorts]: [[Compiling on macOS using MacPorts]]. | |||
== Raspberry Pi == | |||
:''See the main page [[Raspberry Pi]].'' | |||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
[[Category:Installation]] | [[Category:Installation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 30 July 2024
General
- Note: For compilation of GRASS GIS source code, see Compile and Install
This page explains the installation of GRASS binaries.
GRASS GIS requires a workstation running either some flavor of UNIX conforming to POSIX standards like Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, IRIX, or BSD or MS-Windows. It is also possible to run GRASS in MS Windows by using UNIX translation software such as Cygwin or natively with MingGW. Ideally, you should have at least 500 Mb for data and 512 Mb RAM. The source code package needs around 270 MB uncompressed. The resulting binaries may need between 20 MB and 180 MB depending on your platform. During a full compilation you may need temporarily up to 150MB including the source code.
The Software Download Section of the main GRASS web site contains the latest binaries and source code for all supported platforms. That site also has general directions for installing GRASS manually. However, installation is slightly different on each operating system. Here you can find user-contributed pointers for installing GRASS on specific platforms. In particular, many operating systems have package management utilities that can greatly simplify GRASS installation.
MS Windows
- The official download page GRASS GIS for MS-Windows
There are two main flavours:
- OSGeo4W installer, for a broad set of open source geospatial software packages including GRASS GIS as well as many other packages (QGIS, GDAL/OGR, and more). Advantage: whenever you run again the OSGeo4W installer, it updates the existing installation.
- Standalone winGRASS installer: install GRASS GIS with the required support packages.
OSGeo4W installer
OSGeo4W is an installer for a broad set of open source geospatial software packages including GRASS GIS as well as many other packages (QGIS, GDAL/OGR, and more). Advantage: whenever you run again the OSGeo4W installer, it updates the existing installation.
- Install using OSGeo4W installer which installs all dependencies as well (PROJ, GDAL, GEOS, Python, etc.)
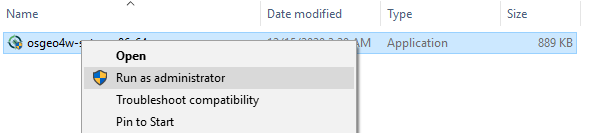
Launch the OSGeo4W installer
Save the downloaded installer (consider to keep it for future updates) and run it as an administrator. You can select either the grass (stable) or grass-daily (development) packages to install.,
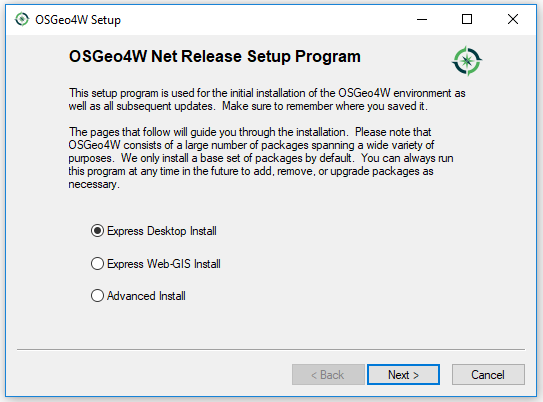
Variant A) Express installation
Use "Express Desktop Install" mode to select stable version.
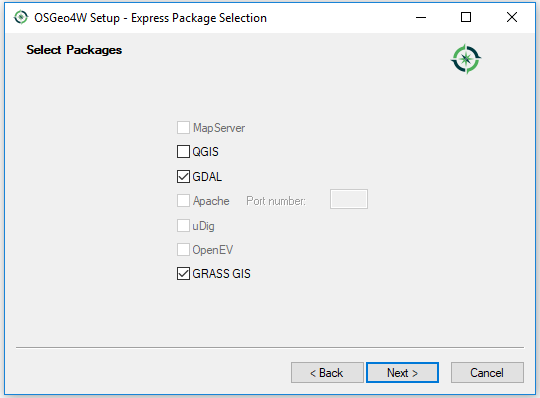
Common installed Python packages:
- python3-gdal
- python3-matplotlib
- python3-wx
- python3-numpy
- python3-pillow
- python3-pip
- python3-ply
- python3-pyopengl
- python3-psycopg2
- python3-six
- python3-pywin32
Additional useful packages (e.g. python3-pandas, msys) can be installed in "Advanced Install" mode.
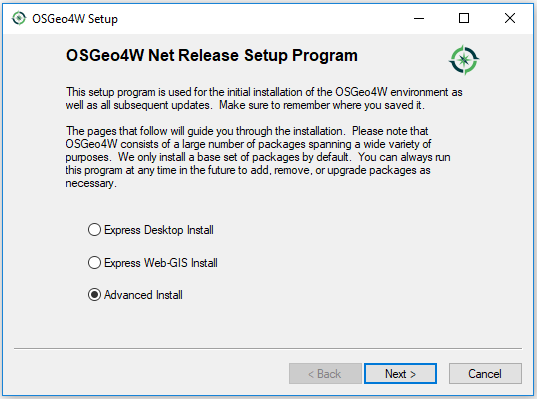
Variant B) Advanced installation
Use "Advanced Install Mode" to select development version.
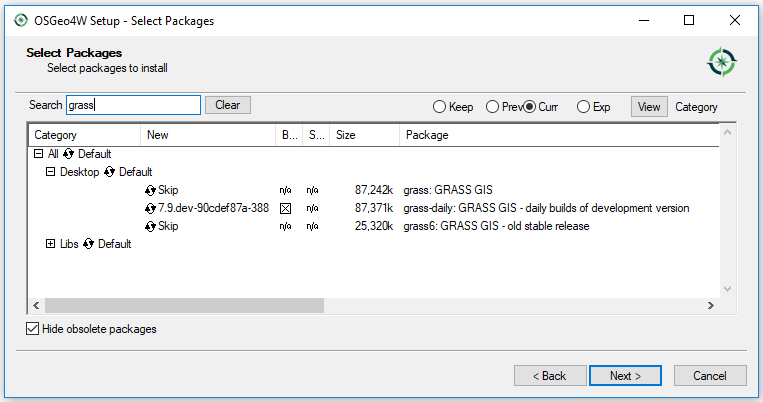
winGRASS standalone installer
- Native winGRASS package installer is available here.
QGIS with winGRASS installer
- QGIS including native winGRASS packages are provided here.
GNU/Linux
- The official page GRASS GIS Download for GNU/Linux
Debian
A binary version of GRASS is available from the apt repository. As root type:
apt-get install grass grass-doc
This is the easiest way to install GRASS on Debian. If you choose to install a binary version manually from the main web site, be sure to follow the instructions for making symlinks found as a note to the [GRASS GIS stable weekly snapshot] release.
DebianGIS
There is also the wonderful DebianGIS project which has a more recent GRASS version with its related packages. Read here for more details
Compiling GRASS from source
- See Compile and Install of Source Code
Installation on Fedora
The Fedora project provides RPM-packages for stable releases prepared to install on Fedora systems:
sudo dnf install grass grass-gui
Mageia
- Mageia provides PROJ/GDAL/GRASS RPMs:
urpmi grass
openSUSE
- openSUSE provides GRASS and related RPM-packages:
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper install grass
Alternatively, one can use the One-Click installer: https://software.opensuse.org/package/grass
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL, CentOS and EPEL)
- Fedora offers GRASS and related binaries for CentOS and EPEL
dnf install grass
Ubuntu
GRASS Binaries are available from apt/synaptic. From a terminal type:
sudo apt-get install grass grass-doc
or alternatively, search for and install these packages from Synaptic. This is the easy way to get GRASS on your system. Even if you choose to install binaries from another source, you may want to install this version just so that all (most) dependencies are installed as painlessly as possible.
To get the latest version of GRASS on Ubuntu, compile the code from source. See the Compile and Install section for a shell script that makes this easy.
MacOS
Precompiled GRASS GIS packages for macOS can be found here. These are distributed as zipped *.dmg packages. Opening the dmg prompts the user to simply drag and drop the app into the Applications folder. In fact, they must be installed into the Applications folder and may not run properly in other locations.
A brief introduction to how to install via MacPorts: Compiling on macOS using MacPorts.
Raspberry Pi
- See the main page Raspberry Pi.