Working with external data in GRASS 7: Difference between revisions
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
380647.5282779|316022.61797616|8 | 380647.5282779|316022.61797616|8 | ||
376739.6982779|315970.62597616|9 | 376739.6982779|315970.62597616|9 | ||
==== Create new empty OGR layer ==== | |||
Check connection settings: | |||
v.external.out -p | |||
dsn: PG:dbname=pgis_nc | |||
format: PostgreSQL | |||
options: <none> | |||
New OGR layer can be created using {{cmd|v.edit}}, note that you need to specify feature type for newly created OGR layer (point, line or area). | |||
v.edit map=pmap tool=create type=point | |||
== Using wxGUI == | == Using wxGUI == | ||
Revision as of 07:55, 24 August 2011
This page explains how to work with external data in GRASS 7.
Raster data
External raster data can be linked via r.external. List of supported formats can be determined by
r.external -f
To link file-based data formats, eg. GeoTiff
r.external input=ncrast/urban.tif output=urban
Vector data
See trac wiki page for development issues.
Link external data
External vector data can be linked via v.external. List of supported formats can be determined by
v.external -f
To link file-based data formats, eg. ESRI Shapefile
v.external dsn=ncshape/ layer=railroads
Assuming that railroads.shp is located in directory ncshape.
To link database-based data formats, eg. PostGIS
v.external dsn=PG:dbname=pgis_nc -l Data source <PG:dbname=pgis_nc> (format 'PostgreSQL') contains 4 layers: bridges ...
v.external dsn=PG:dbname=pgis_nc layer=bridges output=b
Assuming that database pgis_nc has PostGIS layer named bridges. This layer is linked to GRASS mapset as vector map b.
Direct access to external data
External data can be accessed using OGR library via virtual mapset OGR.
v.info map=PG:dbname=pgis_nc@OGR layer=bridges
Create new OGR layers using GRASS modules
v.extract showcase
OGR driver in GRASS 7 also supports write access to the external data. Showcase bellow:
v.external dsn=PG:dbname=pgis_nc layer=bridges output=b
v.out.ascii input=b where="cat < 10" --q
375171.4992779|317756.72097616|1
374247.5192779|317487.13697616|2
380230.2292779|316900.97897616|3
379191.4162779|316419.09697616|4
388958.8222779|316332.04697616|5
375875.2662779|316319.89597616|6
376393.5282779|316155.96797616|7
380647.5282779|316022.61797616|8
376739.6982779|315970.62597616|9
v.external.out dsn=PG:dbname=pgis_nc format=PostgreSQL
v.extract input=b output=b_9 where="cat < 10"
v.external dsn=PG:dbname=pgis_nc -l
Data source <PG:dbname=pgis_nc> (format 'PostgreSQL') contains 5 layers:
b_9
bridges
...
Example of direct access to external data without creating a link
v.out.ascii input=PG:dbname=pgis_nc@OGR layer=b_9
375171.4992779|317756.72097616|1
374247.5192779|317487.13697616|2
380230.2292779|316900.97897616|3
379191.4162779|316419.09697616|4
388958.8222779|316332.04697616|5
375875.2662779|316319.89597616|6
376393.5282779|316155.96797616|7
380647.5282779|316022.61797616|8
376739.6982779|315970.62597616|9
Create new empty OGR layer
Check connection settings:
v.external.out -p
dsn: PG:dbname=pgis_nc format: PostgreSQL options: <none>
New OGR layer can be created using v.edit, note that you need to specify feature type for newly created OGR layer (point, line or area).
v.edit map=pmap tool=create type=point
Using wxGUI
From menu
File -> Link external formats
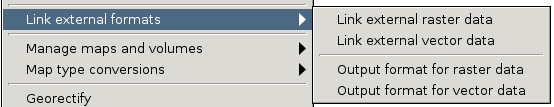
or from toolbar in Layer Manager.