R statistics/rgrass: Difference between revisions
Veroandreo (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(updated, now working) |
||
| Line 249: | Line 249: | ||
== GRASS within R == | == GRASS within R == | ||
To call GRASS GIS 7 functionality from R, use the initGRASS() function to define the GRASS settings: | In the first place, find out the path to the GRASS GIS library. This can be easily done with the following command (still outside of R; or through a system() call inside of R): | ||
grass70 --config path | |||
It may report something like: | |||
/home/veroandreo/software/grass-7.0.svn/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu | |||
To call GRASS GIS 7 functionality from R, start R and use the initGRASS() function to define the GRASS settings: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 255: | Line 262: | ||
# initialisation and the use of North Carolina sample dataset | # initialisation and the use of North Carolina sample dataset | ||
initGRASS(gisBase = "/home/veroandreo/software/grass-7.0.svn", home = tempdir(), | initGRASS(gisBase = "/home/veroandreo/software/grass-7.0.svn/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", home = tempdir(), | ||
gisDbase = "/home/veroandreo/grassdata/", | gisDbase = "/home/veroandreo/grassdata/", | ||
location = "nc_spm_08_grass7", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation", | location = "nc_spm_08_grass7", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation", | ||
override = TRUE) | override = TRUE) | ||
system("g.region - | # set computational region to default (facultative) | ||
system("g.region -dp") | |||
# verify | # verify | ||
gmeta() | gmeta() | ||
| Line 269: | Line 277: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Run | == R in GRASS in batch mode == | ||
Run the following script with | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 275: | Line 285: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
''' | '''To be updated''' | ||
# get path to GRASS binaries: | |||
grass70 --config path | |||
The result is (shorted here): | The result is (shorted here): | ||
| Line 297: | Line 310: | ||
> | > | ||
> # initialisation and the use of spearfish60 data | > # initialisation and the use of spearfish60 data | ||
> initGRASS(gisBase = "/ | > initGRASS(gisBase = "/home/neteler/software/grass70/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", home = tempdir(), gisDbase = "/home/neteler/grassdata/", | ||
+ location = "spearfish60", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation.dem", override = TRUE) | + location = "spearfish60", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation.dem", override = TRUE) | ||
gisdbase /home/neteler/grassdata/ | gisdbase /home/neteler/grassdata/ | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 31 July 2015
This page refers to the usage of R within a GRASS GIS 7 session and the use of GRASS GIS 7 within an R session. (see also R_statistics/spgrass6)
R within GRASS
Startup
- First start a GRASS GIS session. Then, at the GRASS command line start R (for a 'rstudio' session, see below)
- In this example we will use the North Carolina sample dataset.
Reset the region settings to the defaults
GRASS 7.0.1svn (nc_spm_08_grass7):~ > g.region -d
Launch R from the GRASS prompt
GRASS 7.0.1svn (nc_spm_08_grass7):~ > R
Load the rgrass7 library:
> library(rgrass7)
Get the GRASS environment (mapset, region, map projection, etc.); you can display the metadata for your location by printing G:
> G <- gmeta()
gisdbase /home/neteler/grassdata location nc_spm_08_grass7 mapset user1 rows 620 columns 1630 north 320000 south 10000 west 120000 east 935000 nsres 500 ewres 500 projection +proj=lcc +lat_1=36.16666666666666 +lat_2=34.33333333333334 +lat_0=33.75 +lon_0=-79 +x_0=609601.22 +y_0=0 +no_defs +a=6378137 +rf=298.257222101 +towgs84=0.000,0.000,0.000 +to_meter=1
Listing of existing maps
List available vector maps:
> execGRASS("g.list", parameters = list(type = "vector"))
List selected vector maps (wildcard):
> execGRASS("g.list", parameters = list(type = "vector", pattern = "precip*"))
Save selected vector maps into R vector:
> my_vmaps <- execGRASS("g.list", parameters = list(type = "vector", pattern = "precip*"))
> attributes(my_vmaps)
> attributes(my_vmaps)$resOut
List available raster maps:
> execGRASS("g.list", parameters = list(type = "raster"))
List selected raster maps (wildcard):
> execGRASS("g.list", parameters = list(type = "raster", pattern = "lsat7_2002*"))
Reading in data
Read in two raster maps (North Carolina sample dataset):
> ncdata <- readRAST(c("geology_30m", "elevation"), cat=c(TRUE, FALSE), ignore.stderr=TRUE, plugin=NULL)
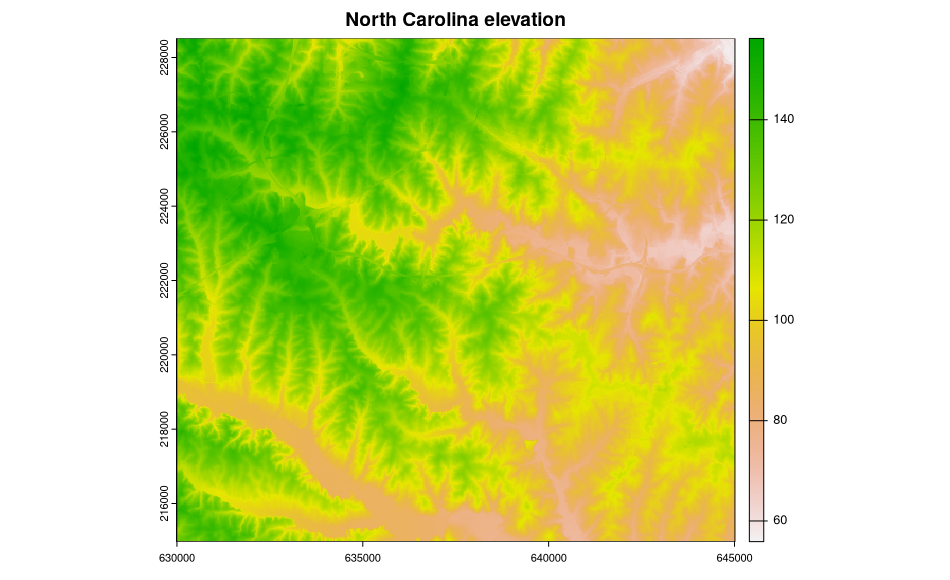
The metadata are accessed and available, but are not (yet) used to structure the sp class objects, in this case a SpatialGridDataFrame object filled with data from two North Carolina layers. Here is a plot of the elevation data:
> image(ncdata, attr = 2, col = terrain.colors(20))
Add a title to the plot:
> title("North Carolina elevation")
In addition, we can show what is going on inside the objects read into R:
> str(G)
List of 26 $ DEBUG : chr "0" $ LOCATION_NAME: chr "nc_spm_08_grass7" $ GISDBASE : chr "/home/veroandreo/grassdata" $ MAPSET : chr "PERMANENT" $ GUI : chr "wxpython" $ projection : chr "99" $ zone : chr "0" $ n : num 228500 $ s : num 215000 $ w : num 630000 $ e : num 645000 $ t : num 1 $ b : num 0 $ nsres : num 27.5 $ nsres3 : num 10 $ ewres : num 37.5 $ ewres3 : num 10 $ tbres : num 1 $ rows : int 491 $ rows3 : int 1350 $ cols : int 400 $ cols3 : int 1500 $ depths : int 1 $ cells : chr "196400" $ cells3 : chr "2025000" $ proj4 : chr "+proj=lcc +lat_1=36.16666666666666 +lat_2=34.33333333333334 +lat_0=33.75 +lon_0=-79 +x_0=609601.22 +y_0=0 +no_defs +a=6378137 +"| __truncated__ - attr(*, "class")= chr "gmeta"
> summary(ncdata)
Object of class SpatialGridDataFrame
Coordinates:
min max
[1,] 630000 645000
[2,] 215000 228500
Is projected: TRUE
proj4string :
[+proj=lcc +lat_1=36.16666666666666 +lat_2=34.33333333333334
+lat_0=33.75 +lon_0=-79 +x_0=609601.22 +y_0=0 +no_defs +a=6378137
+rf=298.257222101 +towgs84=0.000,0.000,0.000 +to_meter=1]
Grid attributes:
cellcentre.offset cellsize cells.dim
1 630018.8 37.50000 400
2 215013.7 27.49491 491
Data attributes:
geology_30m elevation
CZfg_217:70381 Min. : 55.92
CZig_270:66861 1st Qu.: 94.78
CZbg_405:24561 Median :108.88
CZlg_262:19287 Mean :110.38
CZam_862: 6017 3rd Qu.:126.78
CZbg_910: 4351 Max. :156.25
(Other) : 4942
Summarizing data
We can create a table of cell counts:
> table(ncdata$geology_30m)
| CZfg_217 | CZlg_262 | CZig_270 | CZbg_405 | CZve_583 | CZam_720 | CZg_766 | CZam_862 | CZbg_910 | Km_921 | CZbg_945 | CZam_946 | CZam_948 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70381 | 19287 | 66861 | 24561 | 2089 | 467 | 691 | 6017 | 4351 | 1211 | 1 | 398 | 85 |
And compare with the equivalent GRASS module:
> execGRASS("r.stats", flags=c("c", "l"), parameters=list(input="geology_30m"), ignore.stderr=TRUE)
217 CZfg 70381 262 CZlg 19287 270 CZig 66861 405 CZbg 24561 583 CZve 2089 720 CZam 467 766 CZg 691 862 CZam 6017 910 CZbg 4351 921 Km 1211 945 CZbg 1 946 CZam 398 948 CZam 85
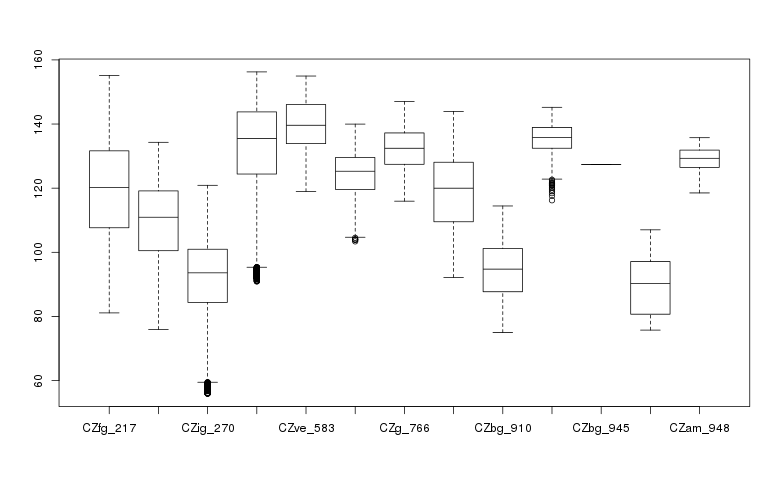
Create a box plot of geologic types at different elevations:
> boxplot(ncdata$elevation ~ ncdata$geology_30m, medlwd = 1)
Exporting data back to GRASS
Finally, a SpatialGridDataFrame object is written back to a GRASS raster map:
First prepare some data: (square root of elevation)
> ncdata$sqdem <- sqrt(ncdata$elevation)
Export data from R back into a GRASS raster map:
> writeRAST(ncdata, "sqdemNC", zcol="sqdem", ignore.stderr=TRUE)
Check that it imported into GRASS ok:
> execGRASS("r.info", parameters=list(map="sqdemNC"))
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Map: sqdemNC Date: Sun Jul 19 13:06:34 2015 | | Mapset: PERMANENT Login of Creator: veroandreo | | Location: nc_spm_08_grass7 | | DataBase: /home/veroandreo/grassdata | | Title: ( sqdemNC ) | | Timestamp: none | |----------------------------------------------------------------------------| | | | Type of Map: raster Number of Categories: 0 | | Data Type: DCELL | | Rows: 491 | | Columns: 400 | | Total Cells: 196400 | | Projection: Lambert Conformal Conic | | N: 228500 S: 215000.0002 Res: 27.49490794 | | E: 645000 W: 630000 Res: 37.5 | | Range of data: min = 7.47818253045085 max = 12.5000787351036 | | | | Data Description: | | generated by r.in.bin | | | | Comments: | | | +----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Calling RStudio from a GRASS GIS session
If you are most used to run R through RStudio, but still want to have all GRASS data available for performing any analyses without loosing the possibility of still using GRASS command line, you can run:
GRASS> rstudio &
or, if you already are working on a certain RStudio project:
GRASS> rstudio /path/to/project/folder/ &
Then, you load rgrass7 library in your RStudio project
> library(rgrass7)
and you are ready to go.
GRASS within R
In the first place, find out the path to the GRASS GIS library. This can be easily done with the following command (still outside of R; or through a system() call inside of R):
grass70 --config path
It may report something like:
/home/veroandreo/software/grass-7.0.svn/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
To call GRASS GIS 7 functionality from R, start R and use the initGRASS() function to define the GRASS settings:
library(rgrass7)
# initialisation and the use of North Carolina sample dataset
initGRASS(gisBase = "/home/veroandreo/software/grass-7.0.svn/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", home = tempdir(),
gisDbase = "/home/veroandreo/grassdata/",
location = "nc_spm_08_grass7", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation",
override = TRUE)
# set computational region to default (facultative)
system("g.region -dp")
# verify
gmeta()
ncdata <- readRAST(c("geology_30m", "elevation"), cat=c(TRUE, FALSE), ignore.stderr=TRUE, plugin=NULL)
summary(ncdata$geology_30m)
R in GRASS in batch mode
Run the following script with
R CMD BATCH batch.R
To be updated
# get path to GRASS binaries: grass70 --config path
The result is (shorted here):
cat batch.Rout
R version 2.10.0 (2009-10-26)
Copyright (C) 2009 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing
ISBN 3-900051-07-0
...
> library(rgrass7)
Loading required package: sp
Loading required package: rgdal
Geospatial Data Abstraction Library extensions to R successfully loaded
Loaded GDAL runtime: GDAL 1.7.2, released 2010/04/23
Path to GDAL shared files: /usr/local/share/gdal
Loaded PROJ.4 runtime: Rel. 4.7.1, 23 September 2009
Path to PROJ.4 shared files: (autodetected)
Loading required package: XML
GRASS GIS interface loaded with GRASS version: (GRASS not running)
>
> # initialisation and the use of spearfish60 data
> initGRASS(gisBase = "/home/neteler/software/grass70/dist.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu", home = tempdir(), gisDbase = "/home/neteler/grassdata/",
+ location = "spearfish60", mapset = "user1", SG="elevation.dem", override = TRUE)
gisdbase /home/neteler/grassdata/
location spearfish60
mapset user1
rows 477
columns 634
north 4928010
south 4913700
west 589980
east 609000
nsres 30
ewres 30
projection +proj=utm +zone=13 +a=6378206.4 +rf=294.9786982 +no_defs
+nadgrids=/usr/local/grass-6.4.1/etc/nad/conus +to_meter=1.0
Warning messages:
1: In dir.create(gisDbase) : '/home/neteler/grassdata' already exists
2: In dir.create(loc_path) :
'/home/neteler/grassdata//spearfish60' already exists
>
> system("g.region -d")
> # verify
> gmeta6()
gisdbase /home/neteler/grassdata/
location spearfish60
mapset user1
rows 477
columns 634
north 4928010
...
>
> spear <- readRAST6(c("geology", "elevation.dem"),
+ cat=c(TRUE, FALSE), ignore.stderr=TRUE,
+ plugin=NULL)
>
> summary(spear$geology)
metamorphic transition igneous sandstone limestone shale
11693 142 36534 74959 61355 46423
sandy shale claysand sand NA's
11266 14535 36561 8950
>
>
> proc.time()
user system elapsed
2.891 0.492 3.412