Vector network analysis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(extended, cleanup, new ideas) |
(+category doc) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
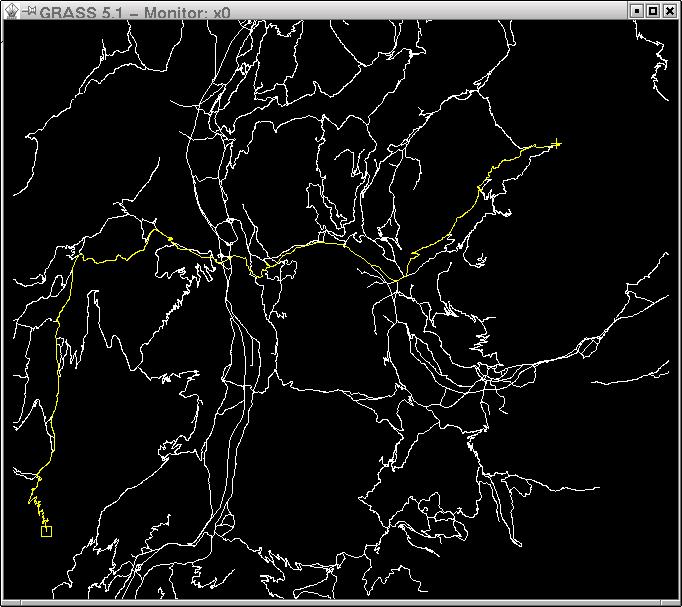
* [http://grass.ibiblio.org/grass63/manuals/html63_user/d.path.html d.path] - Find shortest path for selected starting and ending node. | * [http://grass.ibiblio.org/grass63/manuals/html63_user/d.path.html d.path] - Find shortest path for selected starting and ending node. | ||
[[Image:D.path.jpg]] | [[Image:D.path.jpg]] | ||
[[Category:Documentation]] | |||
Revision as of 21:29, 13 April 2008
Vector network analysis GRASS provides support for vector network analysis. The following algorithms are implemented:
- Vector maintenance: v.net
- Shortest path: d.path and v.net.path
- Traveling salesman (round trip): v.net.salesman
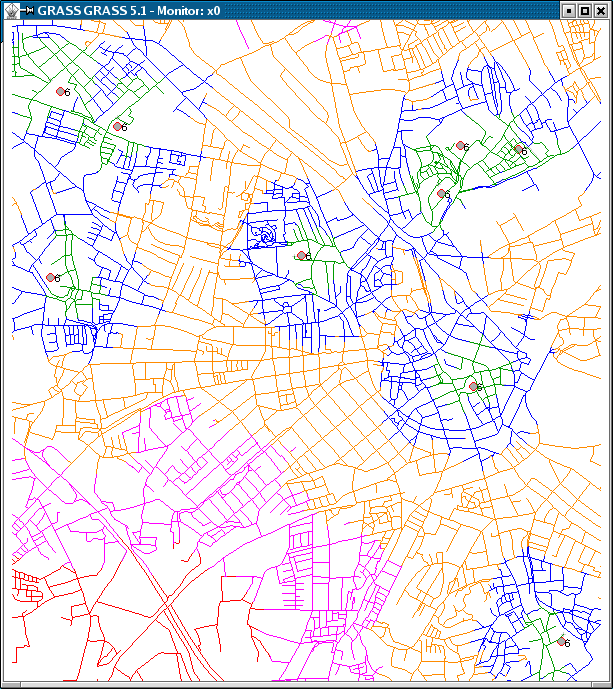
- Allocation of sources (create subnetworks, e.g. police station zones): v.net.alloc
- Minimum Steiner trees (star-like connections, e.g. broadband cable connections): v.net.steiner
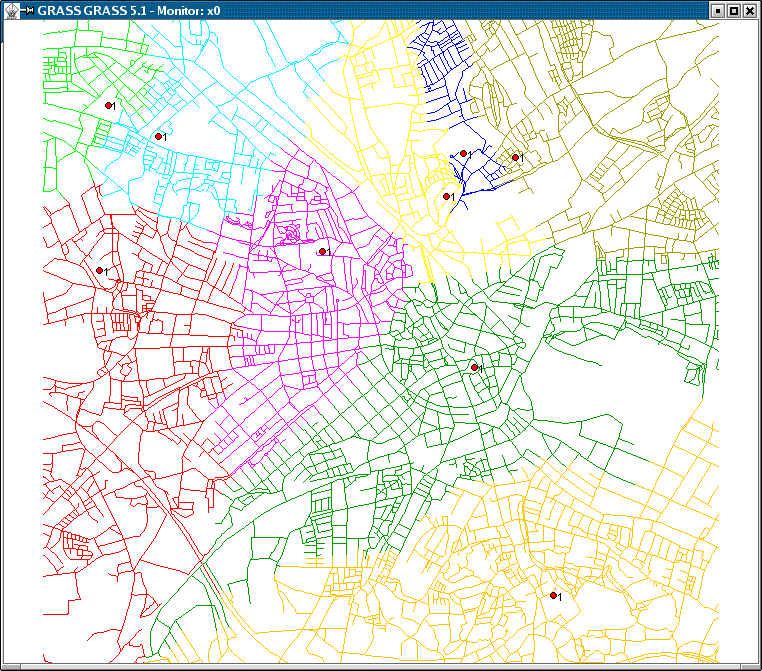
- Iso-distances (from centers): v.net.iso
Vector directions are defined by the digitizing direction (a-->--b). Both directions are supported, network modules provide parameters to assign attribute columns to the forward and backward direction.
- see the vector map processing and network analysis help page
Shortest path routing
- see the v.net.path module and d.path help pages
New ideas
- Vector network analysis ideas (please help to realize)
Screenshots
- more screenshots from the GRASS website
- v.net.iso - Split net to bands between cost isolines (direction from centre). Costs of centre node are used in calculation.
- v.net.alloc - Allocates subnets for nearest centres (direction from centre). Costs of centre node are used in calculation.
- d.path - Find shortest path for selected starting and ending node.