Ps.map scripts: Difference between revisions
(→Script examples: comment out Moldefjord example) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* Example showing all standard vareas [[psmap_fill_patterns|fill pattern hatches]]. (Spearfish dataset) | * Example showing all standard vareas [[psmap_fill_patterns|fill pattern hatches]]. (Spearfish dataset) | ||
<!-- HB 5 Aug 2008: Willem requested this be taken offline, commented out while I clarify. | |||
* [[psmap_moldefjord_example|Commands used to create the geology map of Moldefjord, Norway]] shown on the [http://grass.ibiblio.org/screenshots/cartography.php cartography screenshots page]. | * [[psmap_moldefjord_example|Commands used to create the geology map of Moldefjord, Norway]] shown on the [http://grass.ibiblio.org/screenshots/cartography.php cartography screenshots page]. | ||
--> | |||
* ps.map example demonstrating a [[Psmap_flooding_example|scripted flood risk map]] | * ps.map example demonstrating a [[Psmap_flooding_example|scripted flood risk map]] | ||
Revision as of 04:29, 5 August 2008
Reference manual
You will want to have the ps.map reference manual handy as you will refer to it often. Within the document click on the instruction list links to quickly jump to the section of interest.
- The ps.map help page.
It is suggested to start simply, test the result, and then add more decorations one at a time. The command interface may appear daunting at first but you should get used to it before too long. Manual placement of decorations is a bit of a pain and time-consuming, but it is hoped that there will soon be a new wxGUI map-composer wizard which will act as a front-end to the program, greatly speeding up this part of the task.
Script examples
- Example showing all standard vareas fill pattern hatches. (Spearfish dataset)
- ps.map example demonstrating a scripted flood risk map
- Thematic maps of Belgium
Tips
Multiple raster images
While any number of vector maps can be drawn, ps.map will only let you draw one raster image or RGB image set per map.
- If you want to show two or more overlapping raster maps you need to combine them with the r.patch module or r.mapcalc's '#' color operator.
- (see also the r.his and r.composite modules)
- If you want to show a number of raster maps side by side in a paneled figure you will have to do it in a two step process. The first step is to create each panel as an EPS file, the second step is to include these EPS files in the ps.map command file. Here is an example script demonstrating this.
Placing text below the map box
Use the text instruction with a y coordinate less than 0%. In the same way text can be placed above the map box by using a coordinate greater than 100%. To right justify the text set the x coordinate to 100% and the reference to right.
ps.map out=test.ps << EOF raster elevation.dem text 0% -6% Figure 1.1: Elevation map of Spearfish, SD fontsize 12 ref left end end EOF
Creating a custom info box
The scalebar position and divisions will still have to be set manually, but that just takes a minute if you get the box center coordinate from the gv mouse cursor (see points->inch conversion tip below). For a more simple to use version see the ps.map mapinfo instruction. The same method can be used with the ps.map point and text instructions to create a custom legend.
#... scale 1:100000 scalebar s where 2.4 5.8 length 4000 segment 4 end text 13.5% 16.5% meters background white end text 13.5% 27% SCALE: 1:100,000 background white end rectangle 3.4% 14% 24% 31% fcolor white width 0.5 end #...
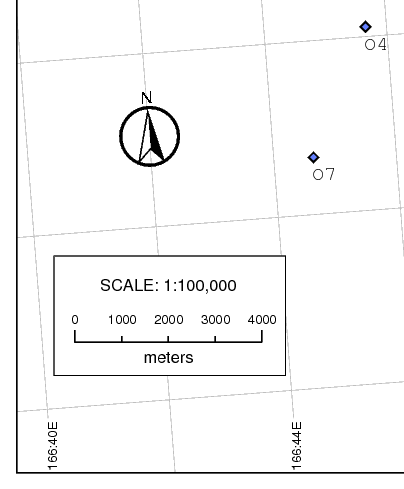
See example in image below.
Creating a fancy North Arrow
You can make a fancy north arrow by combining several ps.map instructions.
In this example we also rotate the north arrow to match true-north instead of the projection's north. This is useful when used with a geo-grid overlay where the grid and the north arrow are right next to each other but don't point in the same direction.
The deviation between true north and the map projection's local +y direction can be obtained from the proj program from PROJ.4. Look for the Convergence angle.
# Spearfish sample dataset # Set the region to match the map to be plotted g.region rast=elevation.dem # find the region's projection information g.proj -pj # find the region's center coordinates in lat/lon g.region -l # Pass this information to the "proj" program echo "103d44'58.937352\"W 44d26'14.761572\"N" | \ proj -V +proj=utm +zone=13 +ellps=clrk66 ... Convergence : 0d52'31.587" [ 0.87544073 ]
We then use this angle with the point (mark symbol) and text instructions' rotate option.
ps.map out=test.ps << EOF raster elevation.dem # 4 arc-minute geo-grid geogrid 4 m color grey width 0.25 numbers 1 end # Fancy N arrow point 84.4% 83% symbol extra/n_arrow1 rotate 0.875 fcolor black size 15 end text 84.2% 90% N rotate 0.875 end point 84.4% 83% symbol basic/circle fcolor none size 35 end end EOF
It is also possible to estimate this angle by reprojecting two points within the map with the same longitude, and then using trigonometry on the resulting coordinates. For example:
g.region -b
...
center latitude: 103:45:00.965601W
center longitude: 44:26:09.69961N
echo -e "103d45'W 44d26N\n 103d45'W 44d27N" | m.proj -i
...
599526.26 4920549.57 0.00
599497.97 4922400.85 0.00
# reverse normal atan2(y,x) as we use CW from north as 0 degrees, not CCW from east for theta
# thus atan2(x2-x1, y2-y1) gives angle in radians
echo "599526.26 599497.97 4920549.57 4922400.85" | \
awk '{print atan2($2-$1,$4-$3) * (180/3.14159265) * -1}'
0.875487
Which is reasonably close to the more trusted value given by the proj software, and good enough for our purposes.
Centering a map of fixed scale
By default ps.map centers the image at the top of the page and adjusts the map scale to suit. If you set a fixed map scale it will then place the map box at the top-left margins. Note that if the scale does not fit on the page it will be adjusted so it does, so keep an eye on it.
A method to recenter a map box with fixed scale follows. It involves the 'gv' program and a hand calculator. It is hoped in future this can be set automatically ... a pain, but you only have to do it once per map. Example uses the Spearfish dataset.
- 1. Run the ps.map process with no scale.
ps.map out=test.ps << EOF raster elevation.dem end EOF Scale set to 1 : 102867. Reading raster map <elevation.dem in PERMANENT> ... PostScript file [test.ps] successfully written.
If you view the resulting PS file you will see it nicely centered, i.e. extending to the left and right margins.
- 2. Change the scale shown by the program up to some nice round number and run ps.map again.
ps.map out=test.ps << EOF raster elevation.dem scale 1:125000 end EOF Scale set to 1 : 125000. Reading raster map <elevation.dem in PERMANENT> ... PostScript file [test.ps] successfully written.
Note the scale is set to what we asked it to be, and the map box is now smaller and justified to the top-left margins.
- 3. Open the map in gv,
gv test.ps
and note a few numbers: the coordinate of the right edge of the paper (596 for A4), the right-hand border of the map box (466 for the above example), and the left edge of the map box (36 in the above example). tip: use the middle mouse button to draw a temporary zoom box in gv.
These numbers are measured in "points", which are 1/72". So the left edge of the map box is at 36pt, or 1/2", the default left margin. - You can use this to convert the cursor coordinate in gv to inches for use with the various ps.map decorations which require placement in inches measured from the top-left corner of the page.
- In the same way a font of size 10 is 10/72" tall, a 72pt font is exactly 1" tall on the printed page.
You can then calculate the map location to use to center the map box by finding the average of the current margins (in points):
avg_margin = ( (page_right - box_right) + box_left ) / 2
And then converting points to inches:
avg_margin / 72.0
So for this example the map should be centered if 1.146" left and right margins are used. Use the maploc instruction to place the map.
ps.map out=test.ps << EOF raster elevation.dem scale 1:125000 maploc 1.146 1.0 end EOF
Voilà!
Converting SVG to EPS
The ps.map eps and vpoints instructions can display an EPS symbol at points on the map. For instructions on how to convert SVG images to EPS using Inkscape, see the symbols help page.
PostScript files are simply plain text files!
To fix typos, insert special characters, etc., you can open the PostScript file in your favorite industrial-strength text editor, search for the text string, make the edit and resave. Much easier then regenerating the graph for something as simple as a spelling mistake or a figure number change.
Converting PostScript to PDF
ps2pdf is a GhostScript wrapper for converting PostScript files to PDF. The default is to create PDF with rasters sampled at 72dpi for viewing on a computer screen. To render at 1200dpi with defaults set for high quality printing, you can add some gs options to the operation:
ps2pdf -dPDFSETTINGS=/preprint -r1200 filename.ps
- See also: Creating High Resolution PDF files for book production with Open Source tools by Markus Neteler.
PDF files are simply containerized PostScript files!
Well, perhaps it is better to say they are an evolution. If you uncompress the PDF file you can edit it just as in the PostScript editing example above, and then recompress when you are done. A nice tool to compress/decompress PDF is pdftk. The pdftk program also lets you do nice things like concatenate a series of PDF pages into a single PDF document, and split a multi-page document into a series of single page PDFs. Very handy for splicing figures into a bigger document.
Integration with other software
You can use 3rd party software to fine-tune and annotate your maps.
- Please populate with tips!
- Translate to many different vector formats for further editing with pstoedit
- -
- -
- Illustrator
- -
- R Statistics
- You can save small graphs as EPS, then display them at point/centroid positions on the map using the eps or vpoints instructions. (see Belgium "ages" example script above)