Vector network analysis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(DGLib link updated) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* see the {{cmd|vectorintro}} "vector map processing and network analysis" help page | * see the {{cmd|vectorintro}} "vector map processing and network analysis" help page | ||
== Shortest path routing == | == Shortest path routing == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 36: | ||
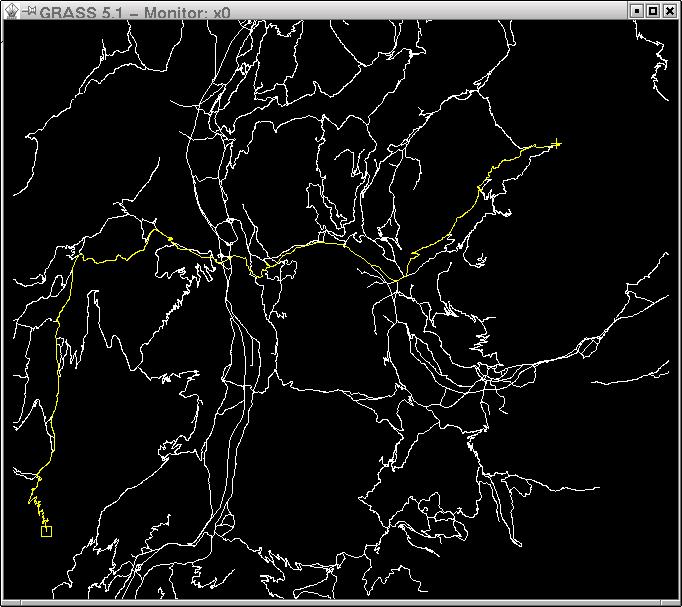
[[Image:D.path.jpg|center|600px|thumb|{{cmd|d.path}} - Find shortest path for selected starting and ending node.]] | [[Image:D.path.jpg|center|600px|thumb|{{cmd|d.path}} - Find shortest path for selected starting and ending node.]] | ||
== See also == | |||
* [[GSoC Network Analysis]]: many new modules! | |||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
Revision as of 17:08, 4 July 2009
Vector network analysis
GRASS provides support for vector network analysis using the DGlib Directed Graph Library.
The following algorithms are implemented:
- Vector maintenance: v.net
- Shortest path: d.path and v.net.path
- Traveling salesman (round trip): v.net.salesman
- Allocation of sources (create subnetworks, e.g. police station zones): v.net.alloc
- Minimum Steiner trees (star-like connections, e.g. broadband cable connections): v.net.steiner
- Iso-distances (from centers): v.net.iso
Vector directions are defined by the digitizing direction (a-->--b). You can navigate either omnidirectionally or differently in each directions as both directions are supported. Network modules provide parameters to assign attribute columns to the forward and backward direction. To see how a vector is directed, use the "display" parameter of d.vect (set display=dir).
- see the vectorintro "vector map processing and network analysis" help page
Shortest path routing
- see the v.net.path and d.path help pages
New ideas
- Vector network analysis ideas (please help to realize)
Screenshots
- more screenshots from the GRASS website
See also
- GSoC Network Analysis: many new modules!