GRASS Debugging: Difference between revisions
m (→Using ldd) |
(→Using Valgrind: save to file) |
||
| Line 244: | Line 244: | ||
** Full memcheck tool, including non-orphaned, but left over, allocated memory: | ** Full memcheck tool, including non-orphaned, but left over, allocated memory: | ||
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=yes --show-reachable=yes $CMD --o | valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=yes --show-reachable=yes $CMD --o | ||
* The default is to send Valgrind output to stderr. Add <tt>--log-file=<filename></tt> to save output to a file, but note (if it matters) that you will lose any interleaved GRASS debug messages from the log that way. | |||
* Valgrind can create PostScript output charts. To convert PostScript to PNG: | * Valgrind can create PostScript output charts. To convert PostScript to PNG: | ||
Revision as of 23:37, 23 July 2009
The following hints assume to work on a working-copy of the GRASS SVN directory.
Additionally it is good to have set the debbugging symbols during compile-time. Do not strip the libraries or use optimization in the compile. see INSTALL and doc/debugging.txt in the source code for more information.
Reporting bugs
- Bugs should be reported in the GRASS bug and wish tracker.
- Please use untranslated messages in your bug reports. The following command will disable the use of translated messages:
export LC_ALL=C
- Users should read the Mailing list etiquette page before posting questions to the grass-dev mailing list.
Patches
- For instructions on creating and applying patches the see Patches wiki page.
Setting GRASS-environment variables (numbers: 1-5)
g.gisenv set="DEBUG=1"
- A higher debug level means you see more messages.
- These messages are always present regardless of compiler settings.
- A setting of "5" is the most verbose, "0" is no debug messages.
Common problems
- Check that the region settings are not totally overwhelming for the raster engine. While there is no set upper limit, anything bigger than 20000x20000 is considered large, and anything an order of mangnitude bigger than that will most likely end with out of memory or large file problems, especially on 32-bit platforms built without LFS support. Many modules will continue to work on these huge datasets, but processing time may make it not worth the while. See Memory issues for more tips.
g.region -p
Watching top
top is a nice command line utility for watching a process's progression. While it won't give you many hard metrics it will give you an idea of what is happening. To make the view a little more stable, with top running from the command line press "M" to sort by memory usage.
Return codes
All GRASS modules send out a return code of "0" if they exit successfully and "1" if they have exited with an error. This is typically accompanied by an "ERROR: " message.
On UNIX (Linux, Macintosh OSX, and Cygwin) directly after a command line module ends you can type "echo $?" and it will tell you the exit code. In a MS-Windows DOS box the equivalent command is "echo %errorlevel%".
Note that some modules (like g.findfile) exit with a status of 1 if it (for example) could not find a file, which may be exactly the test the module was run to perform. In that way the return code can be used in script logic. Thus the exit code only reports EXIT_SUCCESS or EXIT_FAILURE, but a failure can happen for any number of reasons, expected or unexpected, and is not a reason to panic in and of itself.
Using GDB
The GNU Debugger may be used to diagnose Segmentation Faults and other weirdness.
Compile Time Setup
To add debugging information into the built binary, add -g to the CFLAGS arguments.
CFLAGS="-ggdb -Wall -Werror-implicit-function-declaration" ./configure ...
Do not use -O for optimization and do not strip the binaries with LDFLAGS="-s".
Debug symbols for Debian packages
If you are using the Debian package of GRASS the binaries will be stripped at the factory and gcc's -g flag will not have been used in the build. You can however drop in packages from http://debug.debian.net which will be slightly larger and run slightly slower, but will include the debug symbols which make gdb output understandable to us humans.
Using gdb on command line
- Running a program inside GDB works (installation of GDB required :-)
- (e.g. on Debian GNU/Linux: apt-get install gdb)
- Use the exact module name on the command line (at the GRASS prompt) without arguments. Put any command line arguments on the (gdb) command line after the word run.
gdb `which v.in.ogr` run out=some_map dsn="PG:dbname=postgis user=me" olayer=postgislayer
- when it crashes, type "bt full" for a full backtrace
- type "l" to list where in the source code it got to
- type "frame 2" to switch to the second level function (see the backtrace), there you can again type "l" to see where it got up to.
or you can optionally add arguments to gdb directly on the commandline:
gdb --args v.in.ogr out=bla dsn="PG:dbname=postgis user=me" olayer=postgislayer
- Attaching to child process:
- use "attach <pid>" to attach to an existing process (needed for DBMI debugging etc).
- For details, see this hint
Using gdb with a mixed C/TclTK application
You can't invoke gdb directly on "nviz" or $GISBASE/bin/nviz, as that is a shell script. But it's a trivial script which essentially just does:
$GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/nviz -f $GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/scripts/nviz2.2_script ${1+"$@"}
You can debug the $GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/nviz binary as with any other program, i.e.:
$ gdb $GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/nviz > run -f $GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/scripts/nviz2.2_script <any args>
Or, if you don't need to debug the startup, you can start NVIZ then "attach" to the process, as follows:
Once NVIZ is running, get its PID, then:
$ gdb $GISBASE/etc/nviz2.2/nviz > attach <pid> > break Create_OS_Ctx > cont
Selecting the menu option will re-enter the debugger. Single-step through the function (with "next"), printing out the values of any variables as they are assigned.
Using gdb within GNU Emacs
- start GNU Emacs within GRASS session, e.g.
emacs general/manage/cmd/remove.c
- create second buffer by C-x 2
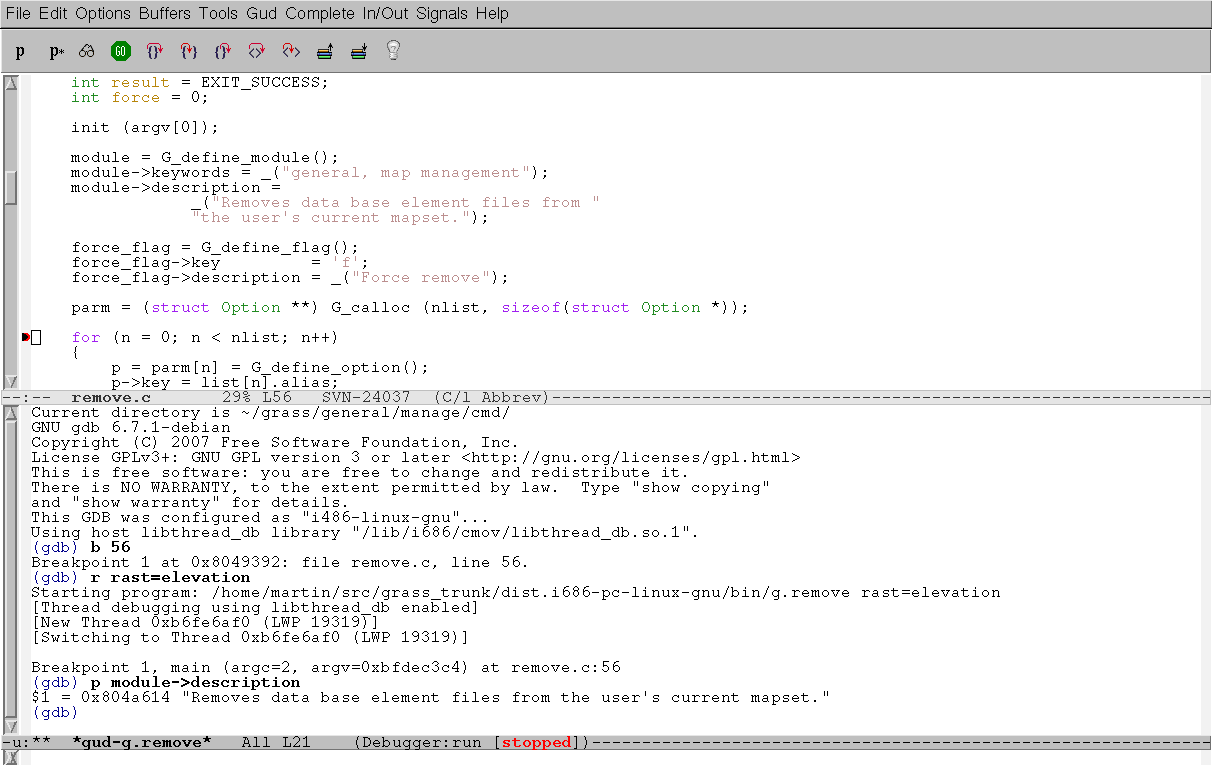
- move cursor to the second buffer by C-x o, then M-x gdb, Enter
- type module name which you would like to debug, e.g. g.remove, Enter
- now you can use gdb inside GNU Emacs
Using DDD (gdb graphical frontend)
- debugging a program inside DDD is rather easy (installation of ddd and gdb required), (on Debian GNU/Linux: apt-get install gdb ddd; on Mandriva: urpmi ddd). Start debugger with GRASS command (e.g., v.in.ogr):
ddd v.in.ogr
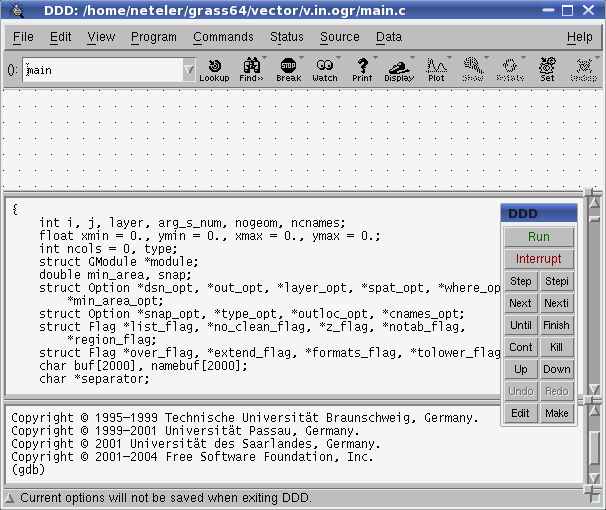
- Run (from main menu PROGRAM): "out=test dsn="PG:dbname=postgis user=me" olayer=postgislayer"
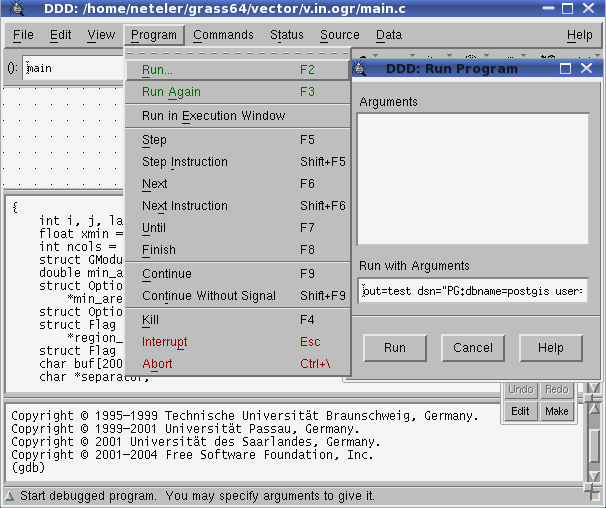
- run with parameters
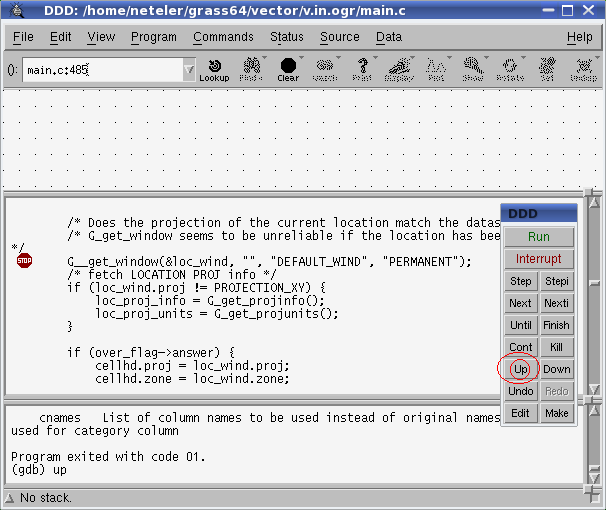
- when it crashes, use the UP menu item to trace back
- reach the line where it crashed
- set a breakpoint, then run again to stop before the crash
- right mouse button on variables permits to display them etc.
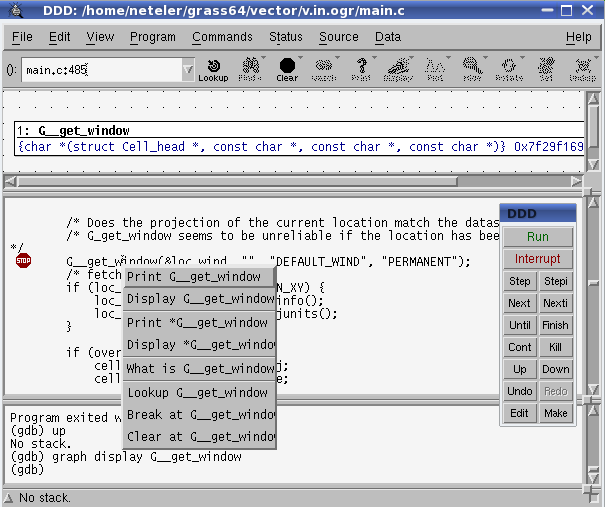
- figure out why it crashed there. This requires PATIENCE. But you will nearly save the world if you identify the problem :-)
Using kdbg (gdb graphical frontend)
- kdbg is not unlike DDD, but it's a KDE application.
- Use is similar to DDD.
- Start with (within GRASS):
kdbg `which g.module`
- Fill in command line arguments with menu item Execution->Arguments.
- Open the View->Locals window.
- Click the Run icon (or Execution->Run) and see where it breaks.
- Set pause-points by clicking a red stop-sign to the left of the "+" on a line of the source code. From there you can step through instructions.
- Explore the values of variables in the locals window.
- You can select an individual variable to watch with
View->Watched expressions
- Type "data" in the text box at the top to view the entire structure of some variable called "data". If it is a structure you can then expand it and click on an interior variable. Clicking on its name makes it come up in the text box. Hit enter from the text box and it will be added to the list of watched expressions. You can edit a Y to X (then enter again) to quickly add another similarly named variable. e.g.:
(data->header).Ycoordinate
Using ldd
On Linux ldd will show the shared library dependencies for a program or library. For example:
For a module:
GRASS> ldd `which v.in.ogr`
For a library:
$ ldd /usr/src/grass/grass-6.2.2/dist.i686-pc-linux-gnu/lib/libgrass_gis.so
The output looks like this:
libz.so.1 => /usr/lib/libz.so.1 (0x40077000)
libgrass_datetime.so => not found
libc.so.6 => /lib/libc.so.6 (0x4008a000)
/lib/ld-linux.so.2 => /lib/ld-linux.so.2 (0x80000000)
In the above example libgrass_datetime.so is missing causing an Illegal Instruction error in libgis. A common error occurs when there are more than one versions of a support library installed, and the GRASS build is using the wrong one. ldd is good for spotting this.
- In Cygwin the "cygcheck" program is used inplace of ldd. See the Cygwin troubleshooting page for information on using that.
- On Mac OSX "otool -L `which v.in.ogr`" almost does the same job.
- For MS Windows the Dependency Walker program (depends.exe) might help.
Library search path
If a support library like libgdal can't be found, and you are sure it is installed, make sure the library search path is set correctly. For example in Linux if GDAL was installed to /usr/local, add the line "/usr/local/lib" to the /etc/ld.so.conf file, and as root run ldconfig to rebuild the library links and cache.
Alternatively you can add the library path to the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH environmental variable.
Using nm and objdump
nm will show a list symbols contained in a library or a program. Use this if you want to check which functions it calls. It will not work if the binary has been stripped.
For example:
GRASS> nm $GISBASE/lib/libgrass_gis.so GRASS> nm `which r.digit`
If the binaries have been stripped you can still use the -D option to show dynamic symbols instead of normal symbols:
$ nm -D /bin/ls
- see also the tools/sql.sh script in the GRASS souce code, which will run "nm" on every object file, library and executable to find dependencies. The result is stored in a PostgreSQL database.
objdump will work even if the binaries have been stripped.
For example:
$ objdump -T /usr/lib/libX11.so $ objdump -R /usr/lib/libX11.so
Using strace
- running the command through strace could give you another hint what is going wrong somewhere.
For example:
strace v.in.ogr out=your_map dsn="PG:dbname=postgis user=me" olayer=postgislayer
Using Valgrind
- Valgrind is a tool to check for memory leaks
(Insert howto here)
Examples:
- analysis of heap usage
CMD="v.in.ascii -zt z=3 in=lidaratm2_250k.txt out=lidaratm2_250k fs=," valgrind --tool=massif --format=html $CMD --o
- analysis of memory leaks (include --trace-children to profile e.g. the DBF driver or other children)
- Full memcheck tool, including non-orphaned, but left over, allocated memory:
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=yes --show-reachable=yes $CMD --o
- The default is to send Valgrind output to stderr. Add --log-file=<filename> to save output to a file, but note (if it matters) that you will lose any interleaved GRASS debug messages from the log that way.
- Valgrind can create PostScript output charts. To convert PostScript to PNG:
- ('pstoimg' is part of the latex2html Debian package)
pstoimg -aaliastext -flip r90 -out massif.550.png -scale 1.3 -crop a massif.550.ps
Using Electric Fence
- Electric Fence checks for bad memory writes, ie specific malloc() over-runs and under-runs.
(Insert howto here)
Example:
CMD="gdalwarp -tps -srcnodata 255 -dstnodata 255 \
-of GTiff -rcs ${TMP}.tif ${OUTFILE}_warp"
LD_PRELOAD=libefence.so.0.0 $CMD
Using a profiling tool
A profiling tool may be used to identify the bottlenecks in long running processes.
Kcachegrind
kcachegrind is a visualization tool for Valgrind's callgrind profiling tool (formerly known as the calltree skin). It is very simple to use. Install the GraphViz package as well.
- The callgrind chapter in the Valgrind user manual
Example:
# Spearfish dataset g.region rast=elevation.dem v.random n=10000 out=rand10k v.db.addtable rand10k column="elev INT" CMD="v.what.rast rand10k rast=elevation.dem column=elev" valgrind --tool=callgrind --trace-children=yes $CMD
This creates a file containing profiling information which kcachegrind can load. We include --trace-children in the above example so we can profile the DBF driver process as well as the main v.what.rast process.
kcachegrind callgrind.out.12345
In the above example from the two process costs we can see that 99.5% is taken by the dbf process and 0.5% is taken by the v.what.rast process. Within the dbf process almost 50% is taken by G_debug() and G_strcasecmp().
gprof
- GNU gprof user guide
- Profiling programs using gprof - article from the Linux Gazzette, March 2004 (#100)
Compile GRASS with -pg flag. E.g.
CFLAGS='-pg' CXXFLAGS='-pg' LDFLAGS='-pg' ./configure --disable-shared
- Example
Run the module
v.select -tg ain=geodetic_swwake_pts bin=urbanarea out=x ope=overlap --o
Use gprof to generate human readable output
gprof ../../dist.i686-pc-linux-gnu/bin/v.select gmon.out > profile.txt
Using Mudflap
GCC built in feature, that "instruments all risky pointer/array dereferencing operations, some standard library string/heap functions, and some other associated constructs with range/validity tests. Modules so instrumented should be immune to buffer overflows, invalid heap use, and some other classes of C/C++ programming errors. The instrumentation relies on a separate runtime library (libmudflap), which will be linked into a program if -fmudflap -lmudflap is given at link time." GCC Wiki
- Requires GCC with mudflap support (GCC 4.x with mudflap USE flag on Gentoo, separate library "libmudflap*" in other distros);
- Add -fmudflap and -lmudflap options (Is this correct way? It works...):
- in include/Make/Platform.make add -lmudflap to LD_SEARCH_FLAGS;
- in include/Make/Platform.make add -fmudflap to CFLAGS1;
- Disable mudflap during compilation
export MUDFLAP_OPTIONS='-mode-nop -viol-nop'
- Compile GRASS (make clean && make). For best results use NO optimisations for compilation (-O0);
- Use GRASS.
- To disable warnings
export MUDFLAP_OPTIONS='-mode-nop -viol-nop'
- To enable warnings
export MUDFLAP_OPTIONS='-mode-check -viol-nop -check-initialization'
More information about debugging with mudflap, can be found here.
Skimming the ChangeLog for changes
- use the tool svn2cl.sh for generating a local changelog-file
Tcl/TK debugging
- Pure Tcl code:
- Typically you need to add "trace" commands to the code in question.
- To debug TCL code which uses C (including hybrid C+Tcl code, e.g. NVIZ, v.digit, run (example):
GRASS:~> g.gisenv set="DEBUG=1" GRASS:~> d.text.freetype > dtf_tcl.txt
then edit 'dtf_tcl.txt' to remove the "| wish &" from the end.
then '. dtf_tcl.txt > dtf.tcl' to get rid of the echo-proofing chars.
then 'wish < dtf.tcl' to test it.
- References:
- "Is white space significant in Tcl" http://wiki.tcl.tk/981
- "Tcl quoting hell" http://wiki.tcl.tk/1726
- "1 minute intro to tcl" http://www.pconline.com/~erc/tcl.htm
Shell script debugging
Add "-x" to the first line of the shell script:
original:
#!/bin/sh
change to:
#!/bin/sh -x
alternatively add `set -x` to somewhere near the start of the script.
Find the script file to edit with
which script
Python script debugging
(please expand)
pdb
Komodo dbgp.client.brk()
from dbgp.client import brk