Vector network analysis
Vector network analysis
GRASS provides support for vector network analysis using the DGlib Directed Graph Library.
Implemented algorithms
The following algorithms are implemented (GRASS 6.5+):
- Vector maintenance: v.net
- Shortest path: d.path and v.net.path
- Shortest path between all pairs of nodes v.net.allpairs
- Allocation of sources (create subnetworks, e.g. police station zones): v.net.alloc
- Iso-distances (from centers): v.net.iso
- Computes bridges and articulation points: v.net.bridge
- Computes degree, centrality, betweeness, closeness and eigenvector centrality measures: v.net.centrality
- Computes strongly and weakly connected components: v.net.components
- Computes vertex connectivity between two sets of nodes: v.net.connectivity
- Computes shortest distance via the network between the given sets of features: v.net.distance
- Computes the maximum flow between two sets of nodes: v.net.flow
- Computes minimum spanning tree: v.net.spanningtree
- Minimum Steiner trees (star-like connections, e.g. broadband cable connections): v.net.steiner
- Finds shortest path using timetables: v.net.timetable
- Traveling salesman (round trip): v.net.salesman
Vector directions are defined by the digitizing direction (a-->--b). You can navigate either omnidirectionally or differently in each directions as both directions are supported. Network modules provide parameters to assign attribute columns to the forward and backward direction. To see how a vector is directed, use the "display" parameter of d.vect (set display=dir).
- see the vectorintro "vector map processing and network analysis" help page
Example: Shortest path routing
- see the v.net.path and d.path help pages
Common parameters
input This is the name of input vector map or data source for direct OGR access.
output This is the name for output vector map.
type This parameter defines arc type, which can be line or boundary.
alayer This parameter is a number and defines the arc layer. Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
nlayer This parameter is a number and defines the node layer. Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
afcolumn This is the number of the cost column for moving in forward direction or forward and backward directions together.
abcolumn This is the number of the cost column for moving in backward direction.
ncolumn This is the number of the cost column for moving through nodes.
Extensios
The Turntable module (to be added to GRASS soon)
New ideas
- Vector network analysis ideas (please help to realize)
Screenshots
- more screenshots from the GRASS website
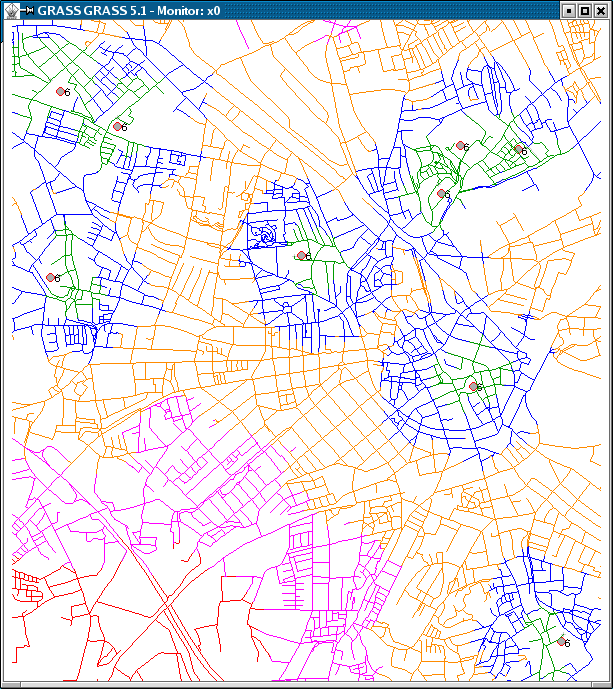
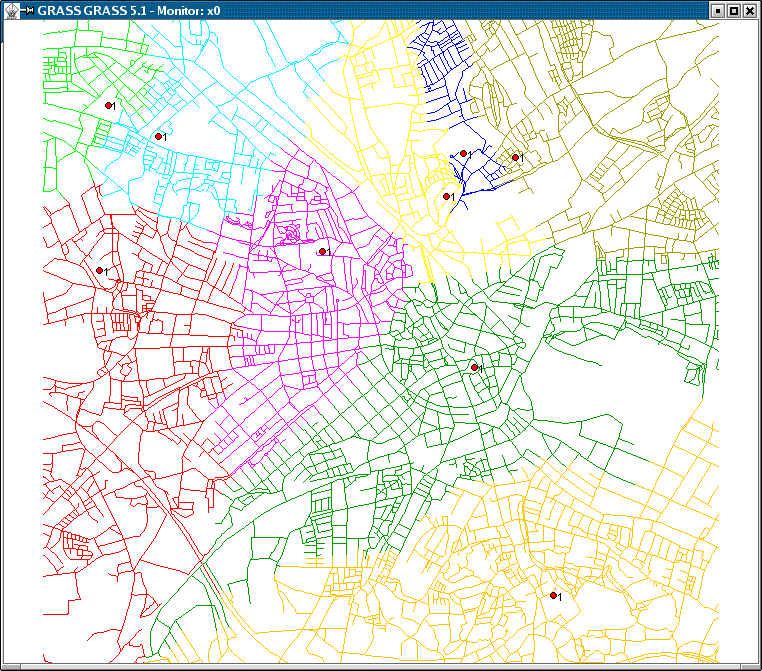
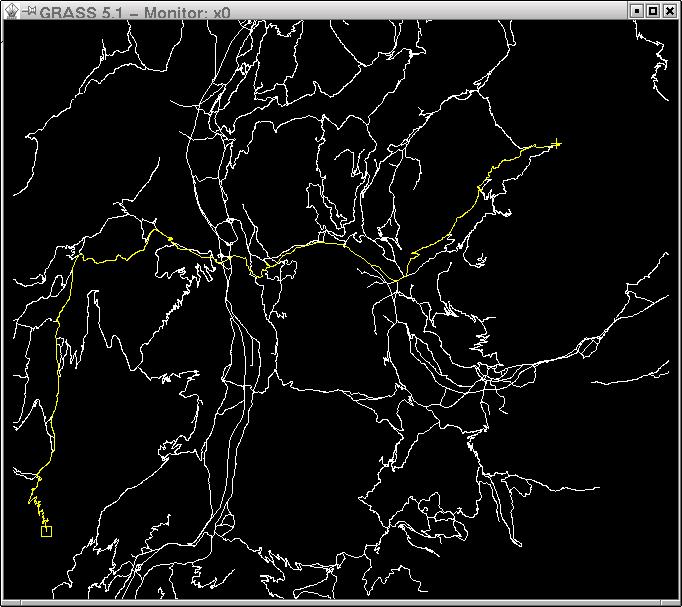
See also
- GSoC Network Analysis: many new modules!
Tutorials
- Network analysis tutorial by University of Trento, Italy