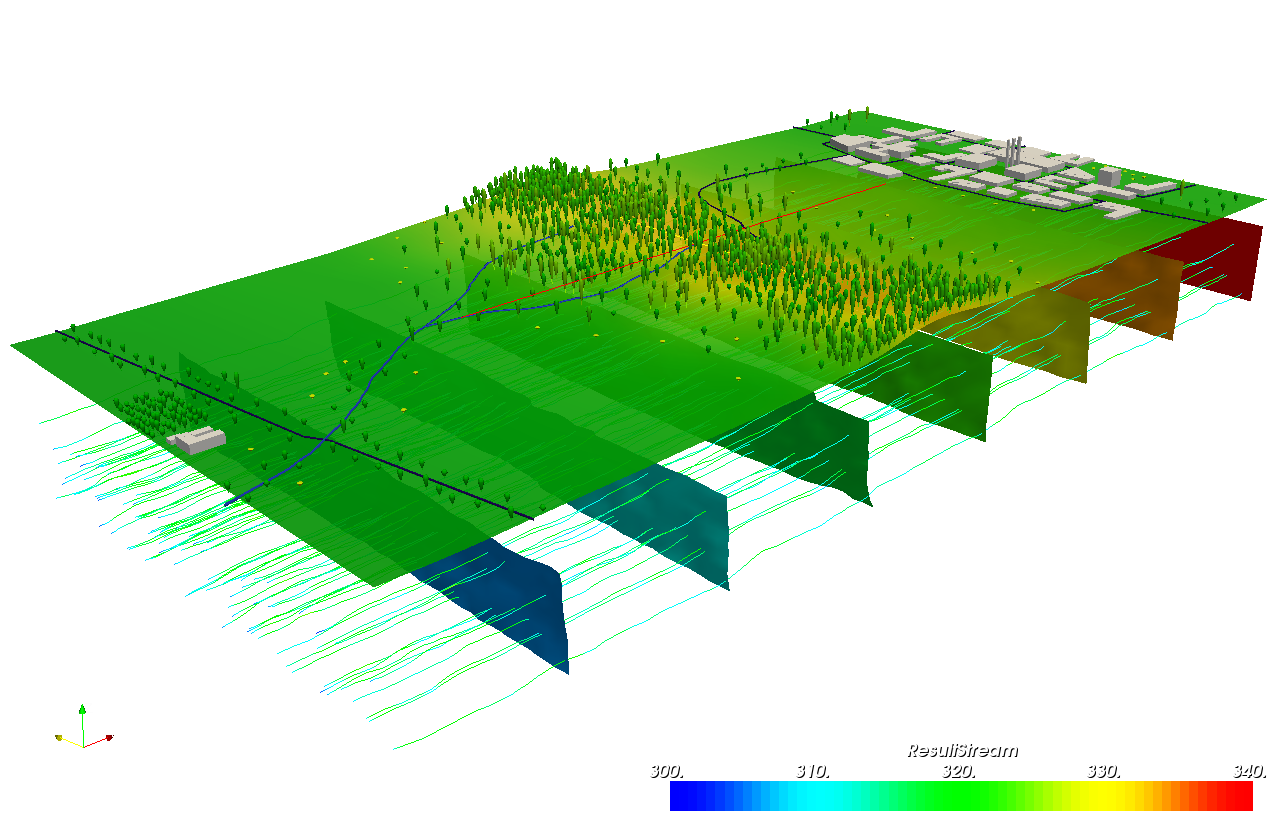
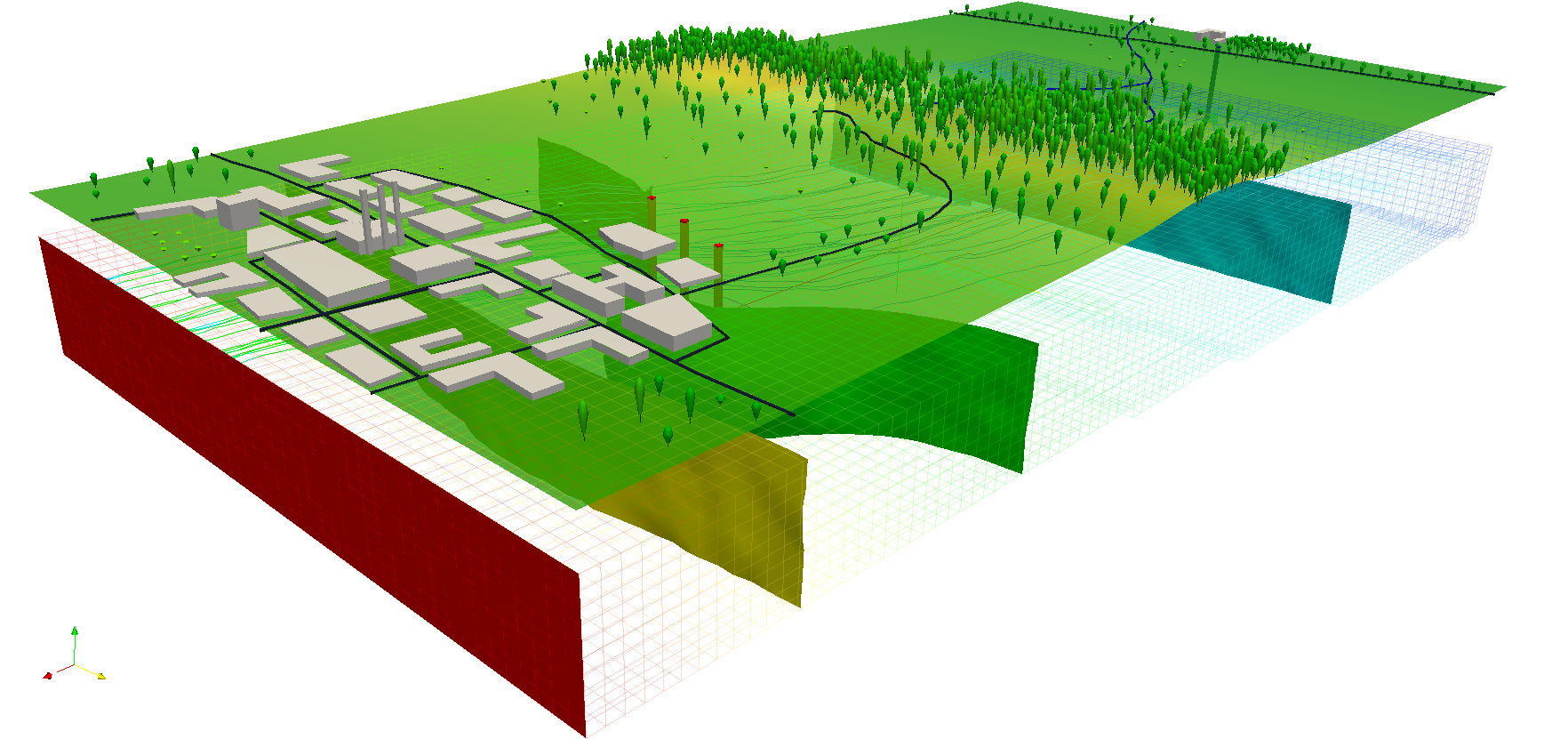
Voxel
3D raster map (voxel) processing in GRASS
GRASS GIS is one of the few GIS with volume data support. Here data are stored as a 3D raster with a unit volume called a voxel (volume pixel). Voxels are designed to support for example representations of trivariate continuous fields.
Import or creating of volumes
From 3D point data:
You can import 3D ASCII raster data in GRASS voxel format using r3.in.ascii or r3.in.xyz (in GRASS 6 an Addon). Note:
- For r3.in.ascii the data need to be plain and properly ordered value data with a header (see the manual for the format).
- In case of regular 3D data (x,y,z,value) in a CSV style file, use r3.in.xyz with method "mean". This only works properly when one value falls into a target voxel.
From 2D raster maps:
You can also create a volume raster model based on 2D raster data by converting 2D raster slices into 3D raster or a 3D volume map based on 2D elevation and value raster maps.
See the raster3dintro for more details.
Voxel operations
Powerful 3D map algebra is implemented in r3.mapcalc.
A 3D groundwater flow model is implement in r3.gwflow.
Cross-sections can be generated with r3.cross.rast.
Voxels can be interpolated from 3D point dat from v.vol.rst.
Voxel statistics
Volume statistics can be calculated with r3.stats and r3.univar.
Visualization
The NVIZ n-dimensional viewer supports voxel visualization. As an alternative, you can use the external Paraview application, see GRASS and Paraview: