Meteorology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Meteorology == | == Meteorology == | ||
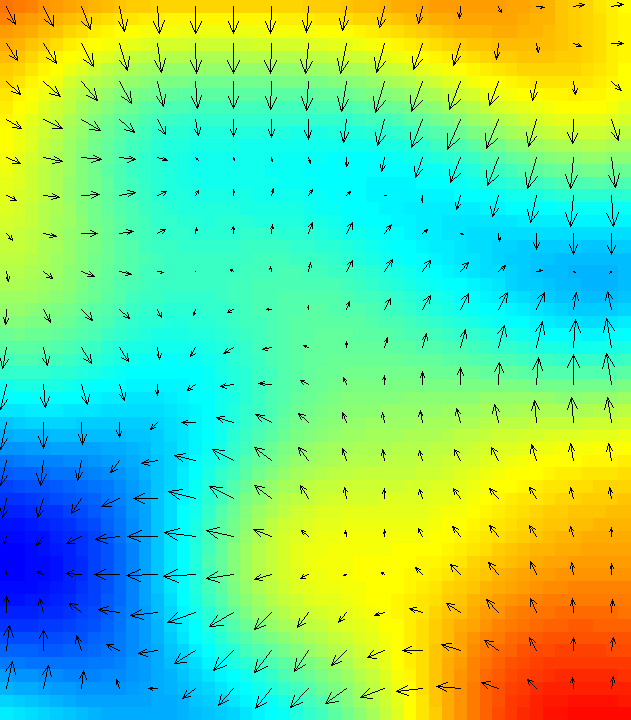
[[Image:D_rast_arrow_magnitude.png|thumb|right|200px|d.rast.arrow at work]] | |||
GRASS used together with [http://grass.osgeo.org/statsgrass/index.php R-stats] provides a powerful toolset to analyse meteorological time series and to perform spatio-temporal interpolation. | GRASS used together with [http://grass.osgeo.org/statsgrass/index.php R-stats] provides a powerful toolset to analyse meteorological time series and to perform spatio-temporal interpolation. | ||
* [[GRIB|Importing GRIB data]] | * [[GRIB|Importing GRIB data]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
* [[IconSymbols#Weather_symbols|Weather symbols]] to use with GRASS display and cartography modules | * [[IconSymbols#Weather_symbols|Weather symbols]] to use with GRASS display and cartography modules | ||
* {{AddonCmd|d.barb}}: Displays wind barbs or variable length straw diagrams given either two raster maps, or vector point data. Like {{cmd|d.rast.arrow}}, input data is given as magnitude and direction, unlike ''d.rast.arrow'' you can also feed it u,v component data. | |||
: See also [http://casoilresource.lawr.ucdavis.edu/drupal/node/989 Visualizing Terrain Surface Indicies with Scaled Arrows]. | |||
* {{cmd|r.in.gdal}} - useful for importing raster data from [http://www.gdal.org/formats_list.html very many source data formats]. | |||
* {{cmd|r.series}} - useful for time series analysis of raster data. | |||
* {{cmd|v.surf.rst}} - useful for 2D spline interpolation between sparse data points. | |||
* {{cmd|v.vol.rst}} - useful for 3D spline interpolation between sparse data points. See the Slovakia 3D precipitation voxel isosurfaces screenshot on the {{website|screenshots/viz.php|visualization screenshots}} page. Tutorial can be found in the [http://www.grassbook.org/data_menu2nd.php GRASS book 2nd Ed.], chapter 7. | |||
== Conventions == | |||
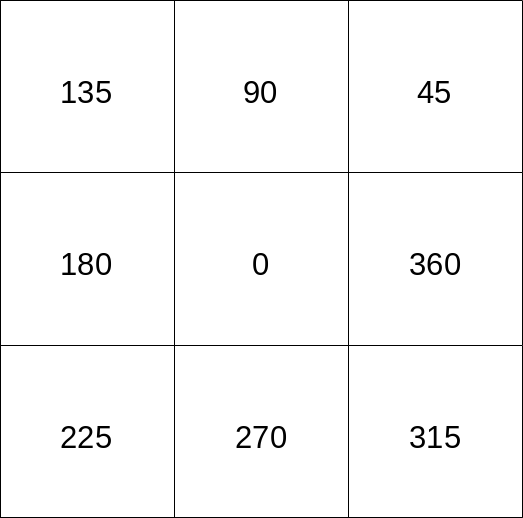
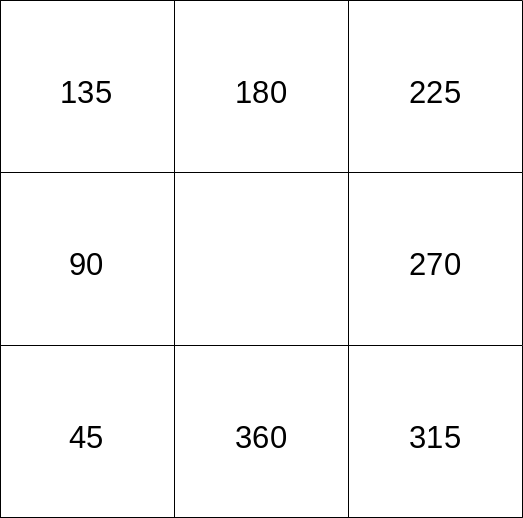
Wind meteorological data usually follow a convention different from the GRASS one. First, the wind direction expresses the direction which wind blows FROM and not TO. Second, the convention on directions differs from the one adopted by GRASS (for aspect, flow direction, etc.), which is the mathematical or Cartesian convention: CCW from the +x axis. | |||
<center> | |||
<gallery perrow=3 widths=300> | |||
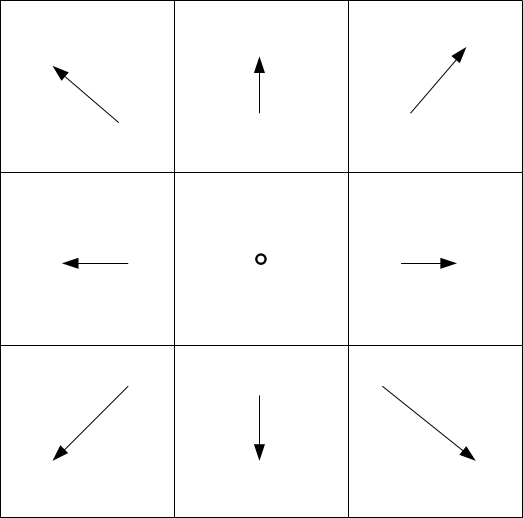
File:Directions.png|Directions | |||
File:Directions_grass.png|Directions according to GRASS convention | |||
File:Directions_wind.png|Directions according to main wind data providers | |||
</gallery> | |||
</center> | |||
[[Category:Applications]] | |||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
[[Category:Grib]] | |||
[[Category:Angle Conventions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:38, 19 July 2015
Meteorology
GRASS used together with R-stats provides a powerful toolset to analyse meteorological time series and to perform spatio-temporal interpolation.
- Weather symbols to use with GRASS display and cartography modules
- d.barb: Displays wind barbs or variable length straw diagrams given either two raster maps, or vector point data. Like d.rast.arrow, input data is given as magnitude and direction, unlike d.rast.arrow you can also feed it u,v component data.
- r.in.gdal - useful for importing raster data from very many source data formats.
- r.series - useful for time series analysis of raster data.
- v.surf.rst - useful for 2D spline interpolation between sparse data points.
- v.vol.rst - useful for 3D spline interpolation between sparse data points. See the Slovakia 3D precipitation voxel isosurfaces screenshot on the visualization screenshots page. Tutorial can be found in the GRASS book 2nd Ed., chapter 7.
Conventions
Wind meteorological data usually follow a convention different from the GRASS one. First, the wind direction expresses the direction which wind blows FROM and not TO. Second, the convention on directions differs from the one adopted by GRASS (for aspect, flow direction, etc.), which is the mathematical or Cartesian convention: CCW from the +x axis.
-
Directions
-
Directions according to GRASS convention
-
Directions according to main wind data providers