SOD Spread tutorial
r.pops.spread is a model for stochastic landscape spread of the pest and pathogens. It uses PoPS (Pest or Pathogen Spread) library. In this tutorial we will use it specifically to model the spread of Sudden Oak Death tree disease. This tutorial shows how to run the model. You can download the sample dataset and simulate sudden oak death spread in the Rouge River-Siskiyou National Forest region of western Oregon.
Software
Required software includes:
- GRASS GIS >=7.2
- Addon module:
Input data used in this tutorial
Download the sample dataset containing:
- digital elevation model
- orthophoto of study area
- study boundaries
- host layer
- layer of all trees
- mapset containing moisture and temperature coefficients
The sample dataset is a GRASS GIS Location, so it goes into your GRASS GIS Database which is usually a directory called grassdata in your home directory or your Documents directory.
Workflow
Download sample data and unzip it. Launch GRASS GIS and select the unzipped Oregon directory, Location Oregon_spread and create a new Mapset tutorial.
Install addon:
g.extension r.pops.spread
First, we will set computational region of our analyses to an extent covering our study area and so that the cells are aligned with our host raster:
g.region vector=EU1_12x8 align=host -p
Create files with lists of input maps
Here we used already prepared weather coefficients, these can be created using this workflow. We need two text files, one with temperature coefficients and one with precipitation coefficients. List and write the maps in a file using g.list. Search for ppt for precipitation and tmean or temperature mean for temperature, we list only the years we need for the simulation (2016 to 2021):
g.list -m type=raster pattern="*ppt_201[6-9]*,*ppt_202[0-2]*" mapset=weather output=precipitation.txt
g.list -m type=raster pattern="*tmean_201[6-9]*,*tmean_202[0-2]*" mapset=weather output=temperature.txt
Compute the spread of SOD for default values
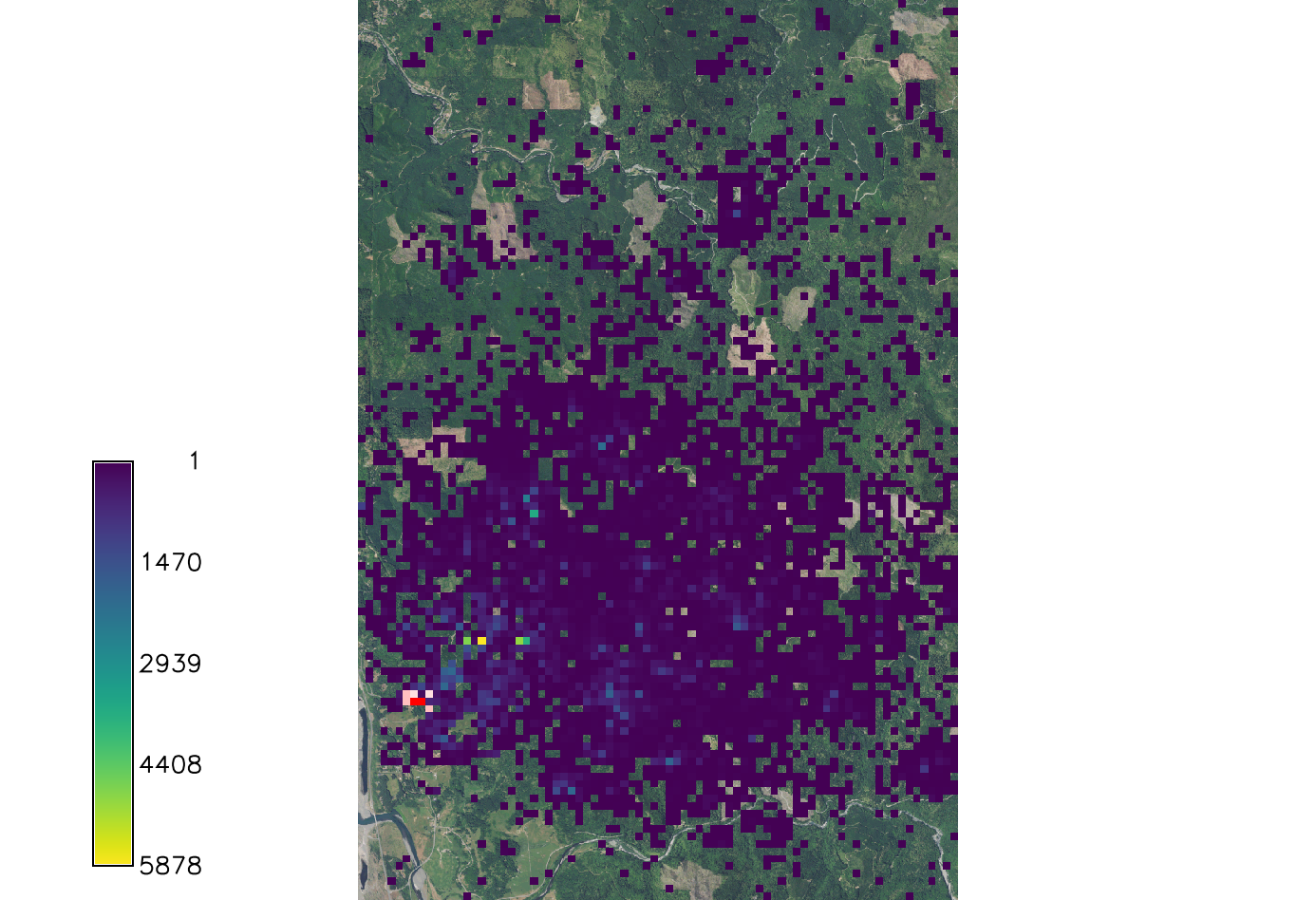
Run the model using the text files created and setting only the required parameters. For this analysis we used a wind direction of NE and are looking at the first 5 years of spread from the initial 2016 infection discovery.
r.pops.spread host=host total_plants=all_trees infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sod output_series=spread_sod wind=NE moisture_coefficient_file=precipitation.txt temperature_coefficient_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 step=week random_seed=4
Add ortho, spread results, and the initial infected area to the display to view the spread. Display only values greater than zero.
d.rast ortho
d.rast -i map=inf_2016 values=0
d.rast -i spread_sod values=0
You can visualize the spread series in Animation Tool.
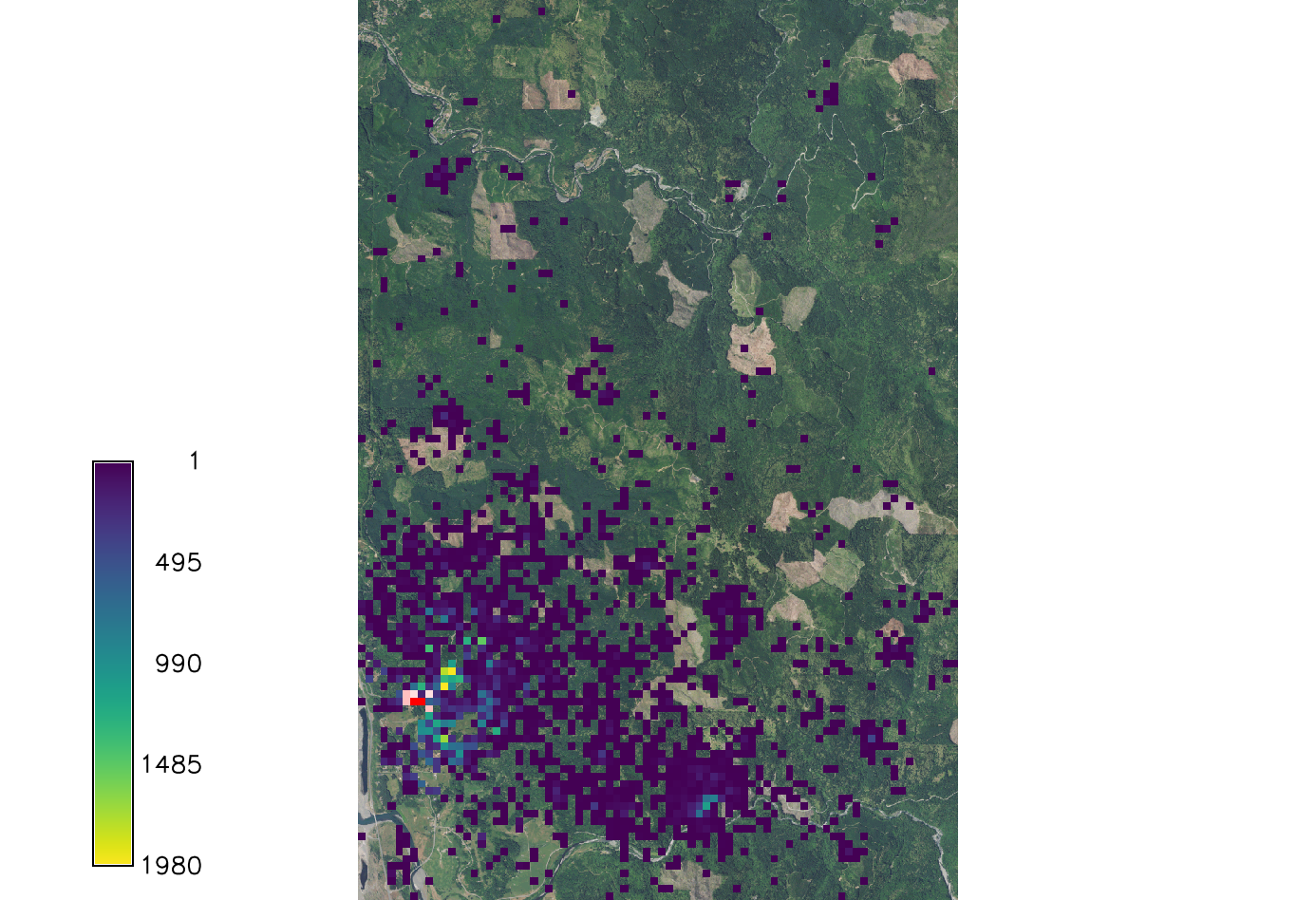
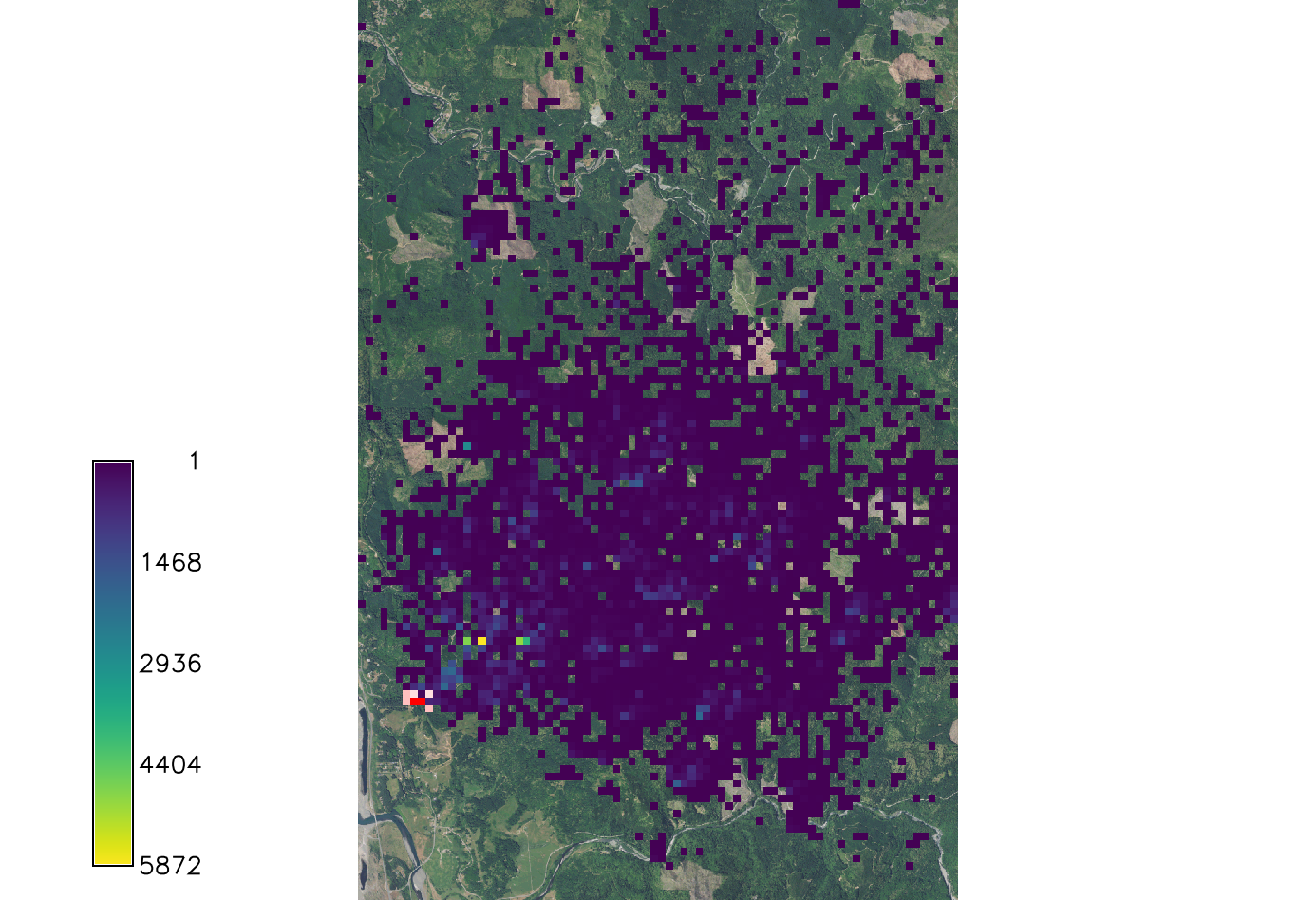
Working with the optional parameters
Wind
Kappa influences the wind dispersal. Wind dispersal uses the Von Mises circular normal distribution. Large kappa makes the distribution very concentrated about the angle, specifically the wind direction specified. If kappa is set to 0 the wind dispersal will have no effect on distribution.
r.pops.spread host=host total_plants=all_trees infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sod_k0 wind=N moisture_coefficient_file=precipitation.txt temperature_coefficient_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 step=week kappa=0 random_seed=4
If k is larger than 2 the distribution becomes very concentrated around the prevailing wind direction.
r.pops.spread host=host total_plants=all_trees infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sod_k4 wind=N moisture_coefficient_file=precipitation.txt temperature_coefficient_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 step=week kappa=4 random_seed=4
Gamma(y)
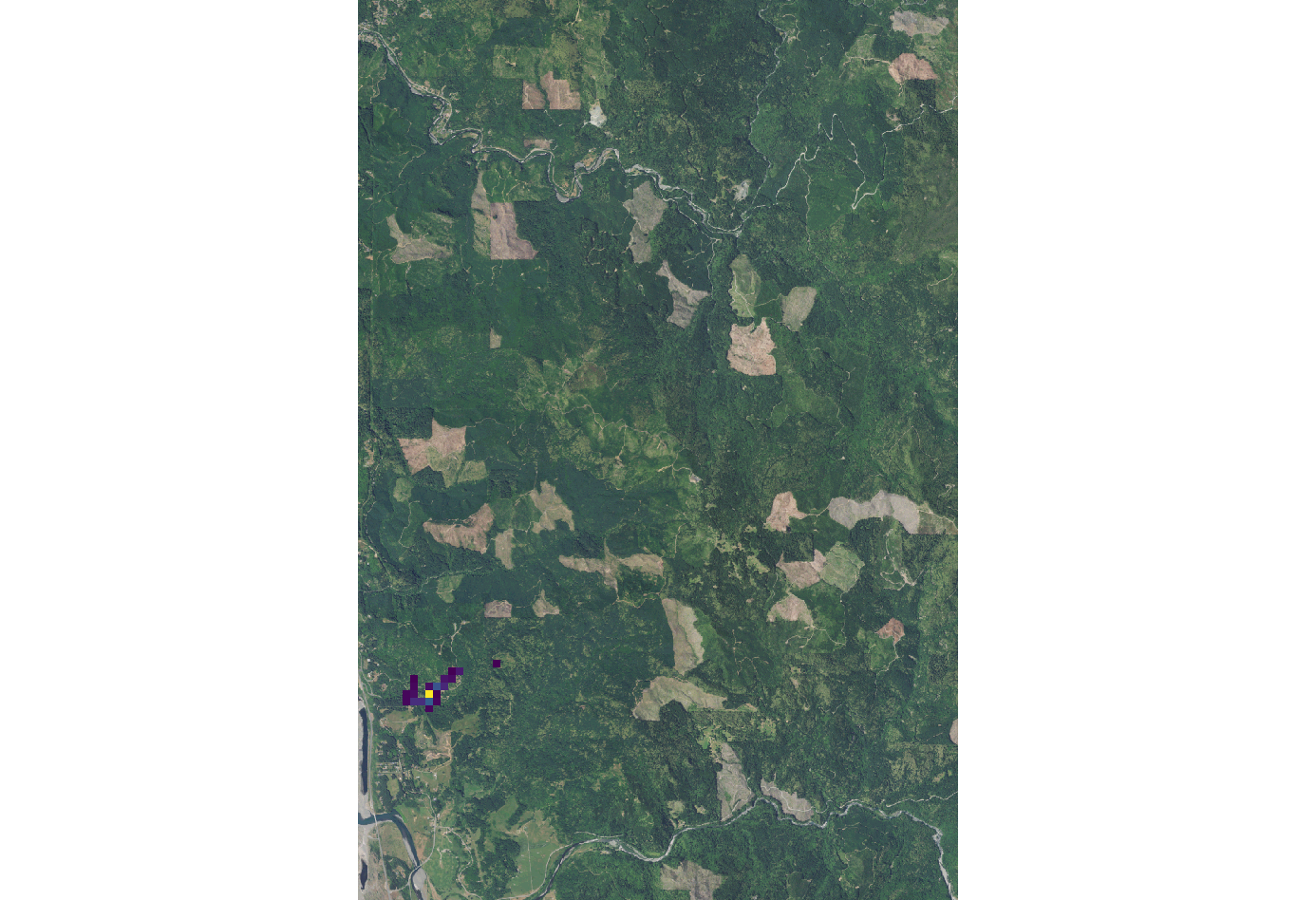


A parameter between 0 and 1 used in the equation for Bernoulli distribution. This parameter is then factored into the Cauchy distribution model for the probability of using the first model. In this instance, a change in the gamma value doesn’t visually affect the output. An example console input for this factor would be:
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sodg1 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 gamma=0.5 random_seed=4
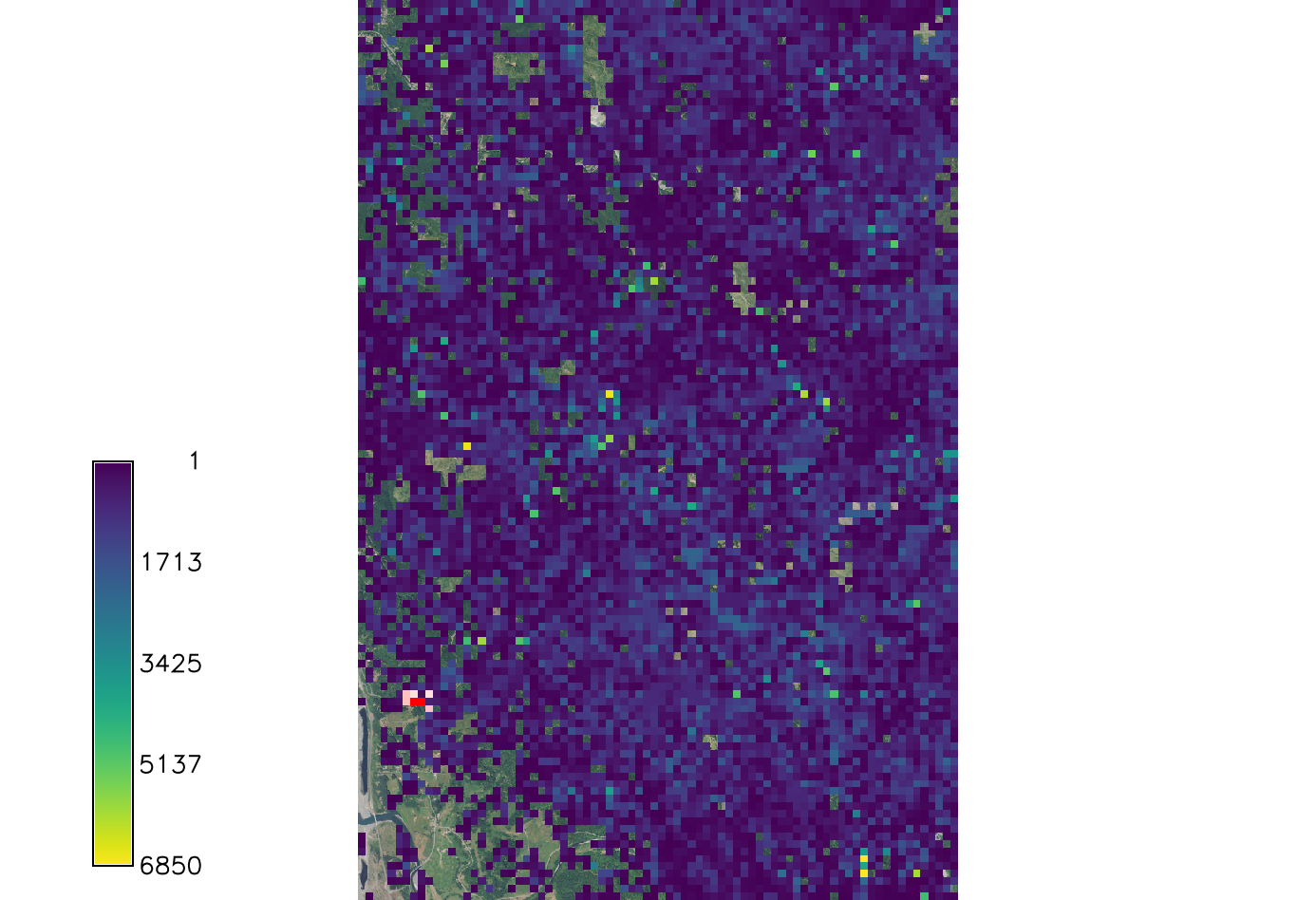
Spore_rate
The spore production rate per week for each infected tree. This model uses the Poisson distribution model to determine the spore rate value. At the time of the initial infection the spores were calculated to spread at a rate of 4.4 spores per week.
Decreasing the rate down to 1 scales down the spread a great deal. However there are still new areas of spread.
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sodsr1 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 spore_rate=1 random_seed=4
Increasing the rate to 10 drastically increases the spread, as to be expected.
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sodsr2 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 spore_rate=10 random_seed=4
Updating these calculations on a regular basis can be done quite easily through the model to better monitor the spread. These values can also be adjusted for distinct locations or different forms of sudden oak death.
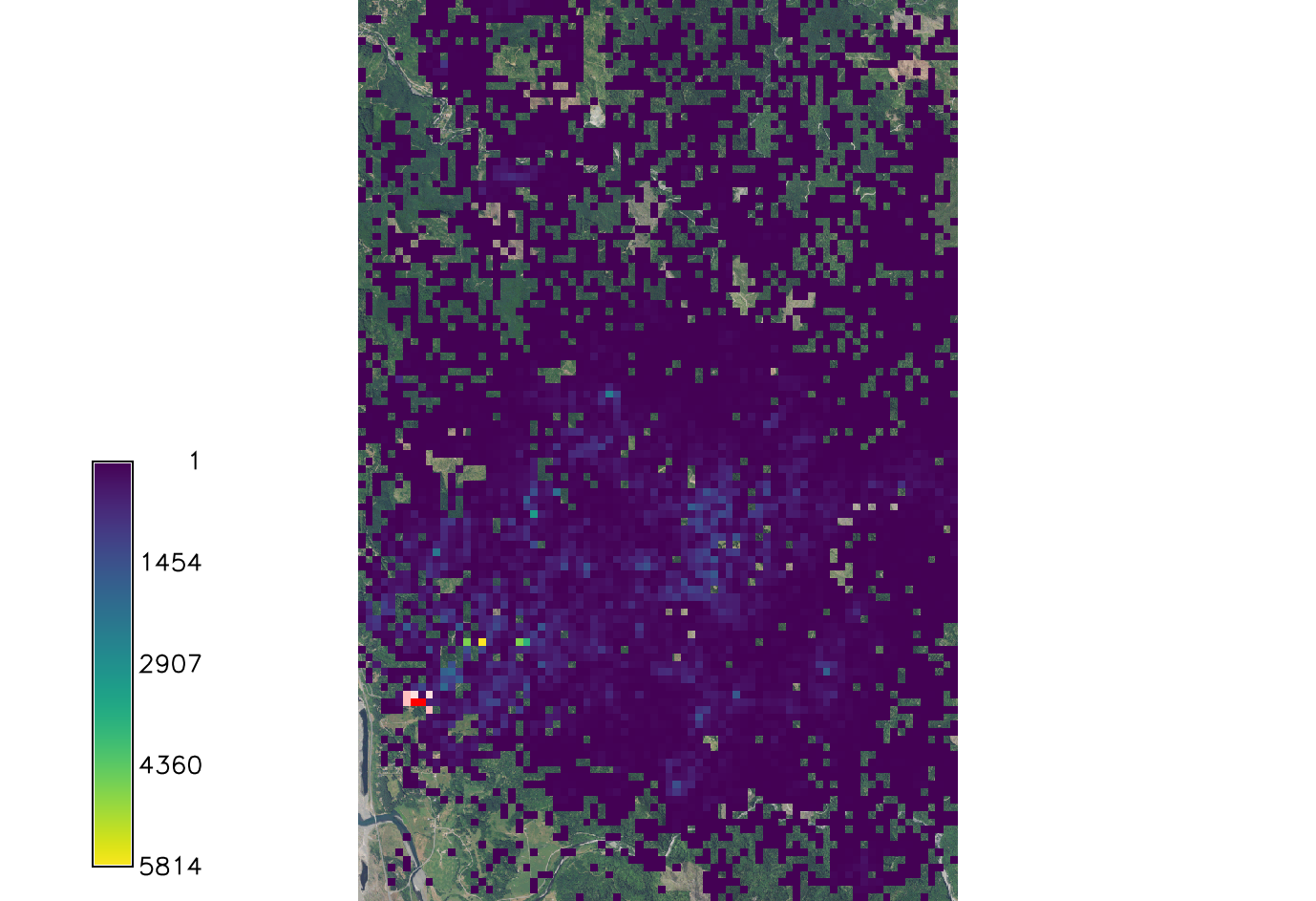
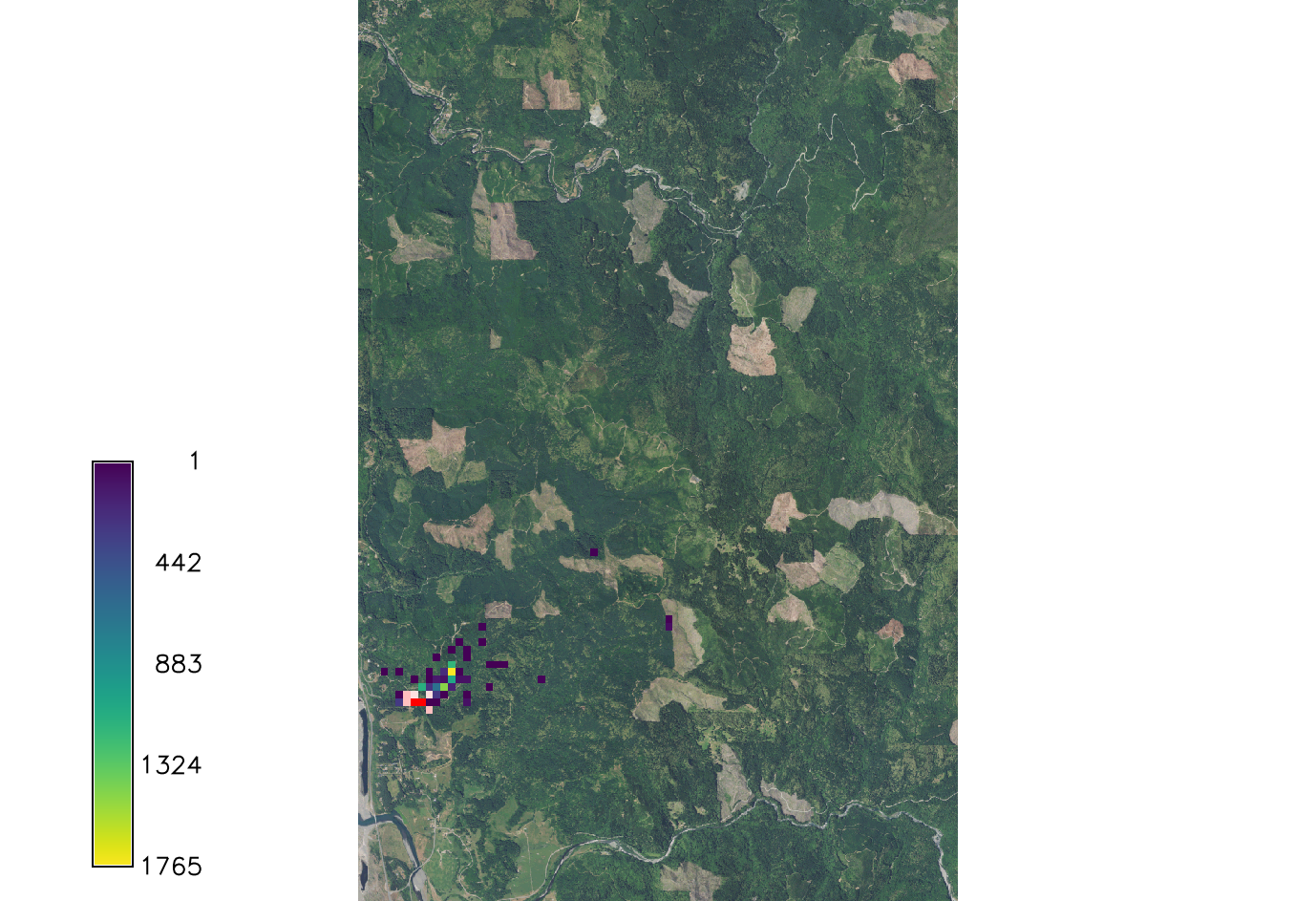

Scale_1 and Scale_2
Parameters dealing with the Cauchy distribution, which is the equation that calculates the continuous random distribution of the spores based on inputs. These scale factors effect the outcome by increasing or decreasing the distribution of the spores. Scale_1 is default set to 20.57 which was found to be the initial spread scale in the western Oregon SOD case.
Setting scale_1 factor to 1 so it has no effect in the equation.
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sods1_1 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 scale_1=1 random_seed=4
Setting scale_1 factor to 50 so it has a greater effect on the spread.
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sods1_2 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 scale_1=50 random_seed=4
Scale_2 is undefined in the equation when the model is run on default. In this instance scale_2 has no visual effect on the output. An example console input for this factor would be:
r.pops.spread species=lide_den_int lvtree=all_den_int infected=inf_2016 output=spread_sods2 wind=NE moisture_file=precipitation.txt temperature_file=temperature.txt start_time=2016 end_time=2021 scale_2=20 random_seed=4